DNA because it has the base AT and GC RNA polymerase is a type of enzyme Enzymes help chemical reactions occur quicklyThe Transcription Student Handout introduces students to the process of transcription They use foam pieces and a placemat to model the transcripton of a DNA template into a singlestranded RNA molecule FGIK Transcription Student Handout Due to an increasing number of students finding answer keys online, we are no longer providing open accessThe transcription of DNA to RNA requires DNA, transcription factors, RNA polymerase and nucleotidesInitially transcription factors assemble a complex on DNA that allow RNA polymerase to bind a promoter sequenceTogether, The procress is somewhat straightforward, with one nucleotide being added to the mRNA strand for every nucleotide read in the DNA strand

41 Dna Transcription Illustrations Clip Art Istock
Model of dna molecule ready for transcription
Model of dna molecule ready for transcription-Gene expression 1 DNA in nucleus serves as a template 2 PremRNA is processed before leaving the nucleus 3 mRNA moves into cytoplasm and becomes associated with ribosomes 4 tRNAs with anticodons carry amino acids to mRNA 5DNA is composed of the bases adenine (A) cytosine , guanine (G), and thymine (T) RNA is composed of adenine, cytosine, guanine, and uracil (U) Is the displayed segment a part of DNA or RNA molecule?



Botany Online Molecular Genetics Transcription
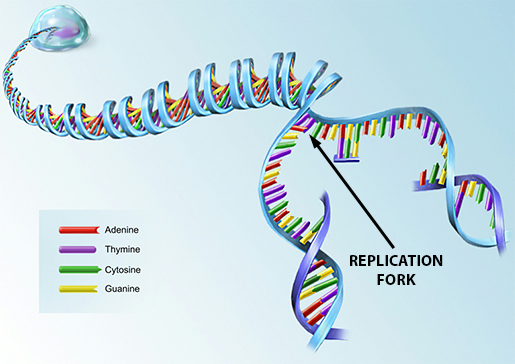
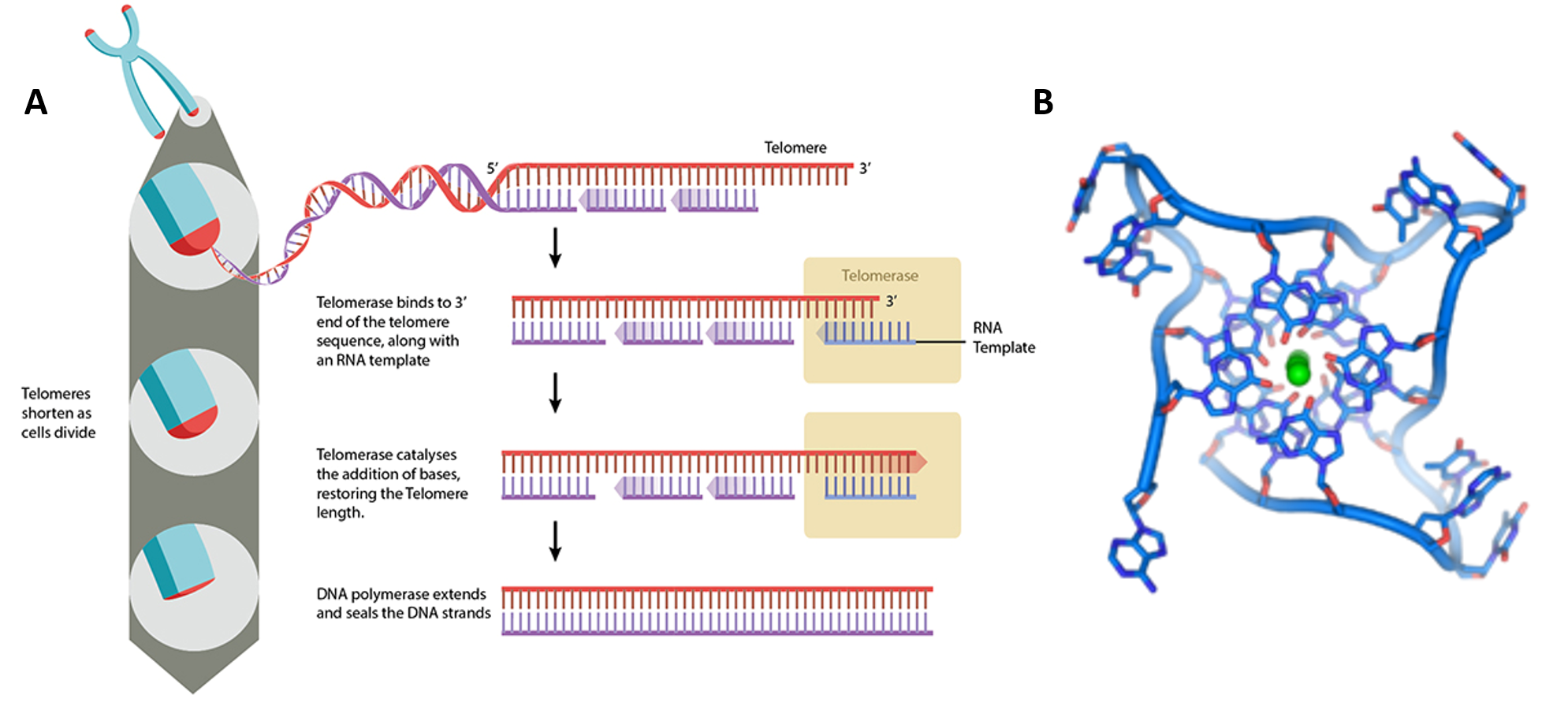
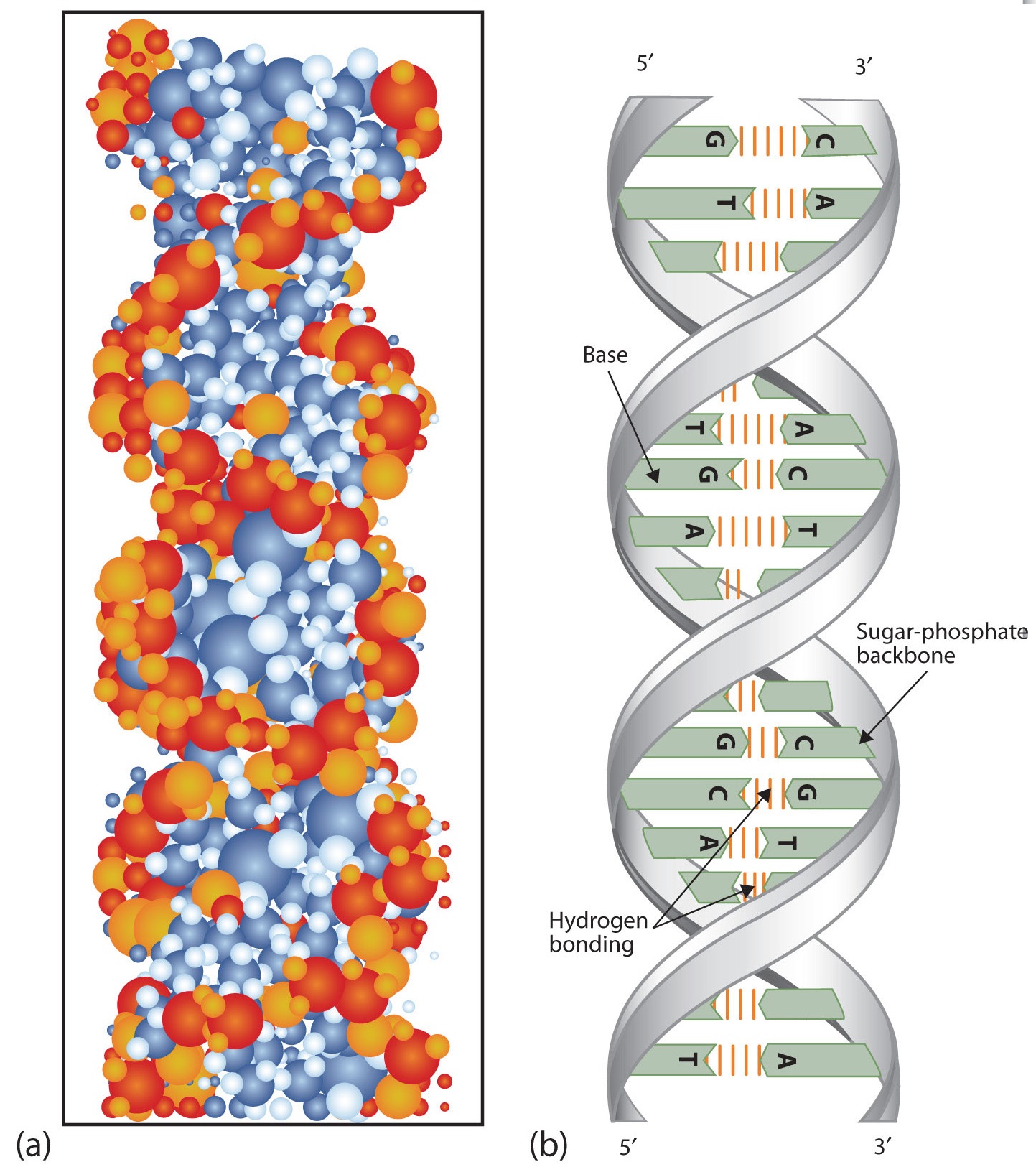
Reverse transcription is the transfer of information from RNA to DNA (the reverse of normal transcription) This is known to occur in the case of retroviruses, such as HIV, as well as in eukaryotes, in the case of retrotransposons and telomere synthesis It is the process by which the genetic information from RNA will be assembled into new DNADna replication, transcription and translation 1 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Figure 167a, c C T A A T CG GC A C G AT AT A T TA C TA 034 nm 34 nm (a) Key features of DNA structure G 1 nm G (c) Spacefilling model T 2The "Dynamic DNA Model" is now available!
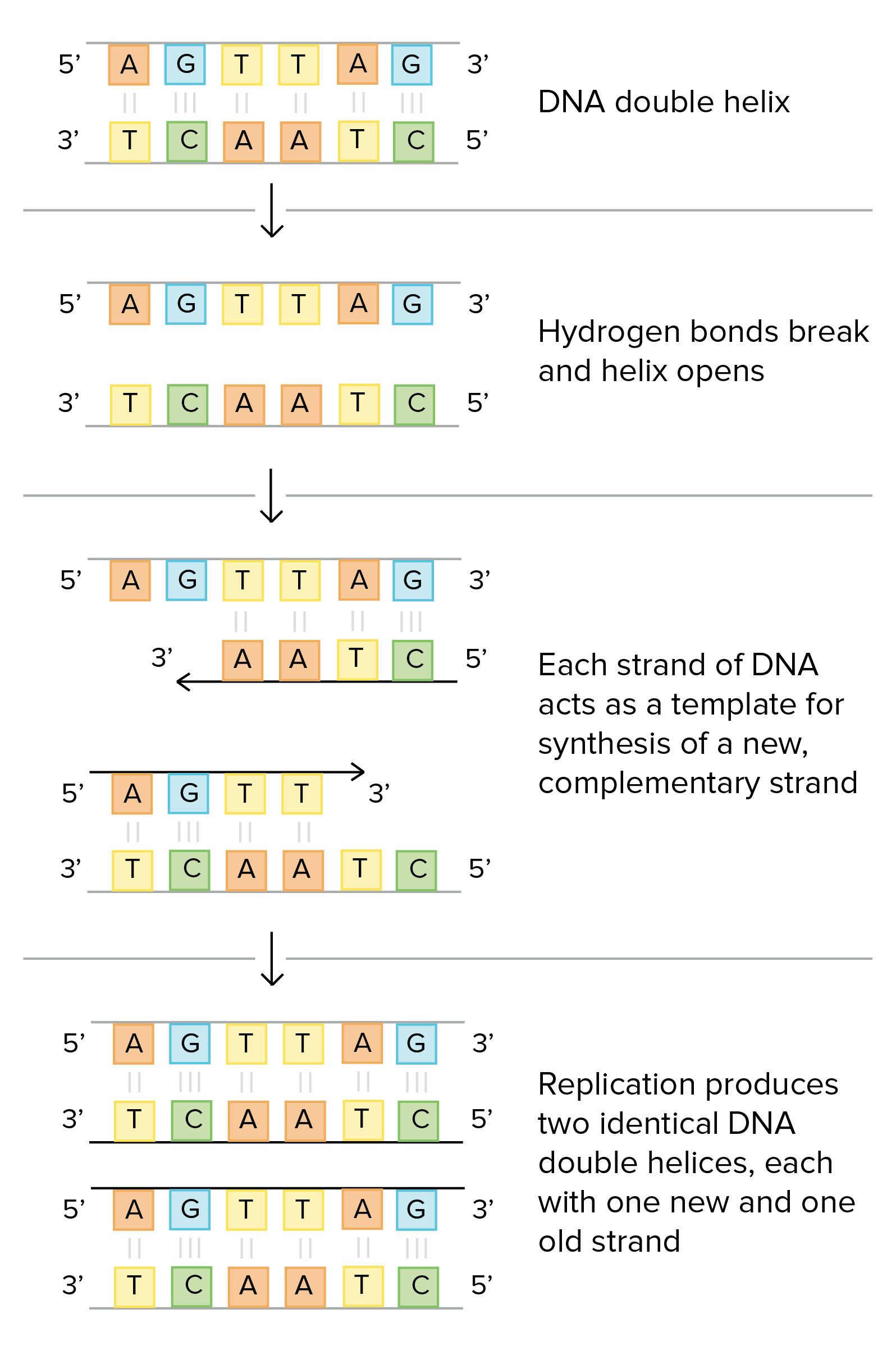
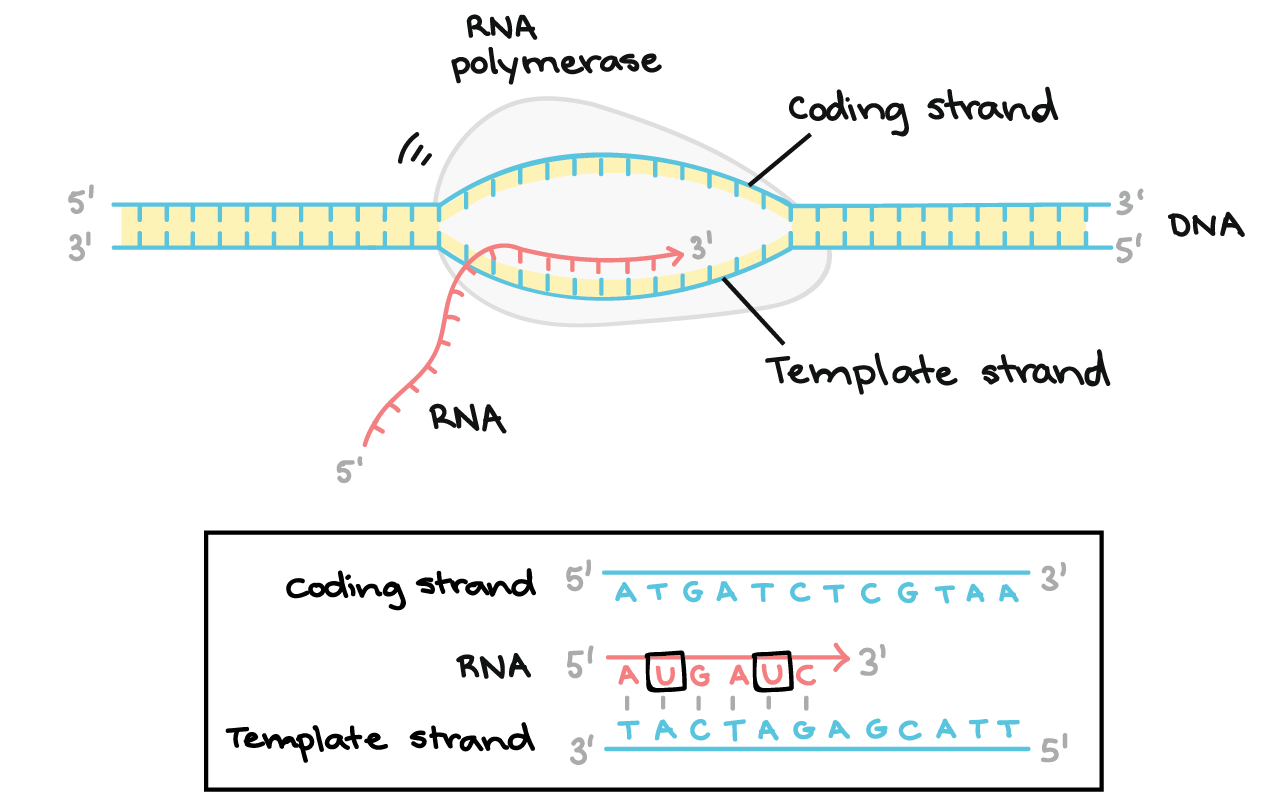
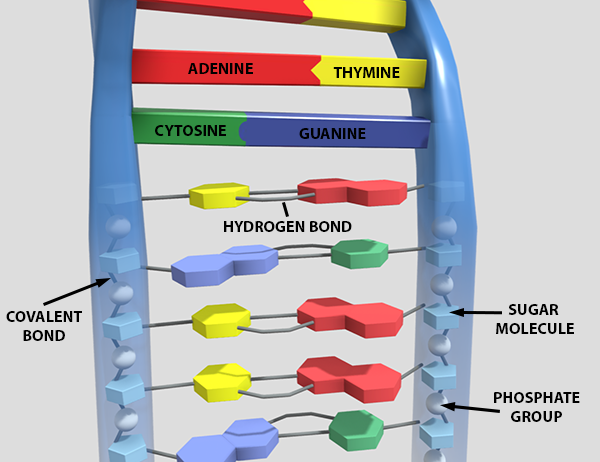
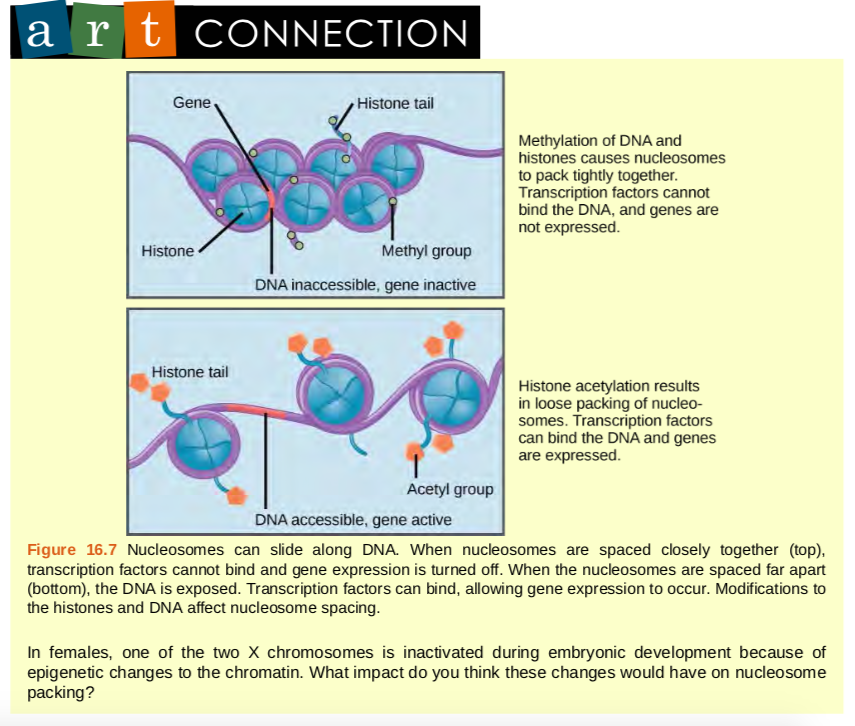
Discuss the experiments leading to the identification of DNA as the molecule that carries the genetic code Describe the steps leading to the development of the doublehelix model of DNA Lesson Summary The Components of DNA DNA is a nucleic acid made up of nucleotides joined into long strands or chains by covalent bondsReplication New cells are continuously forming in the body through the process of cell division For this to happen, the DNA in a dividing cell must be copied in a process known as replicationThe complementary base pairing of the double helix provides aRNA transcription and processing takes place in the nucleus RNA Transcription is the process that copies a DNA sequence into a new RNA sequence, and it is very similar to DNA replication Instead of DNA polymerase, this process uses RNA polymerase to separate the strands and synthesize a new RNA molecule from the DNA template This RNA
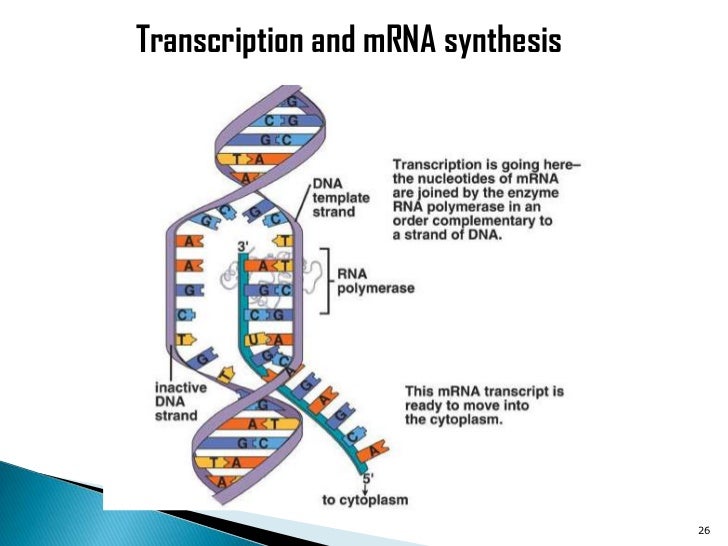
During transcription, the enzyme complex known as _____ _____ creates an RNA molecule by joining nucleotides complementary to a DNA template RNA polymeraser Steps involved in processing primary mRNA to form a mature mRNA molecule39 Transcription from DNA to RNA Both prokaryotes and eukaryotes perform fundamentally the same process of transcription, with the important difference of the membranebound nucleus in eukaryotes With the genes bound in the nucleus, transcription occurs in the nucleus of the cell and the mRNA transcript must be transported to the cytoplasmDNA transcription is a process that involves transcribing genetic information from DNA to RNAThe transcribed DNA message, or RNA transcript, is used to produce proteinsDNA is housed within the nucleus of our cellsIt controls cellular activity by coding for the production of proteins



Molecular Mechanism Of Dna Replication Article Khan Academy



Transcription Of Dna Stages Processing Teachmephysiology
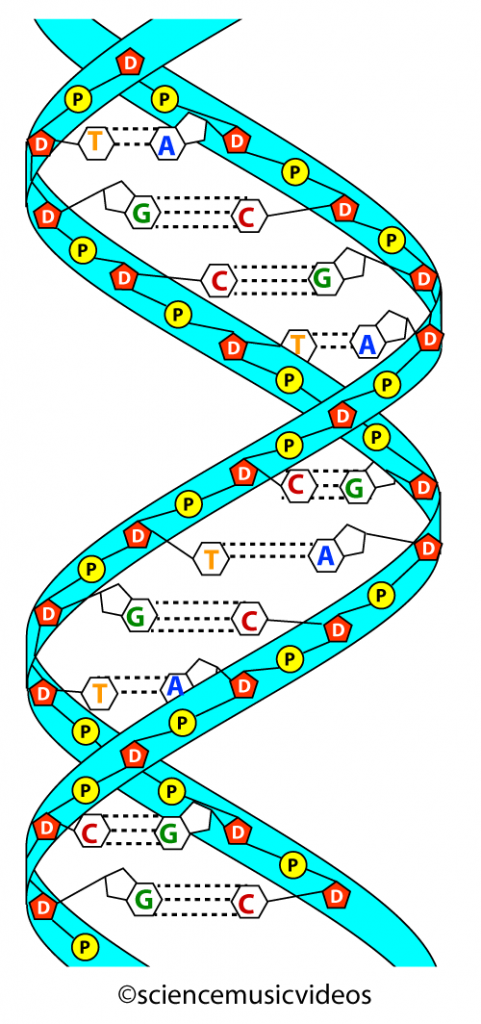
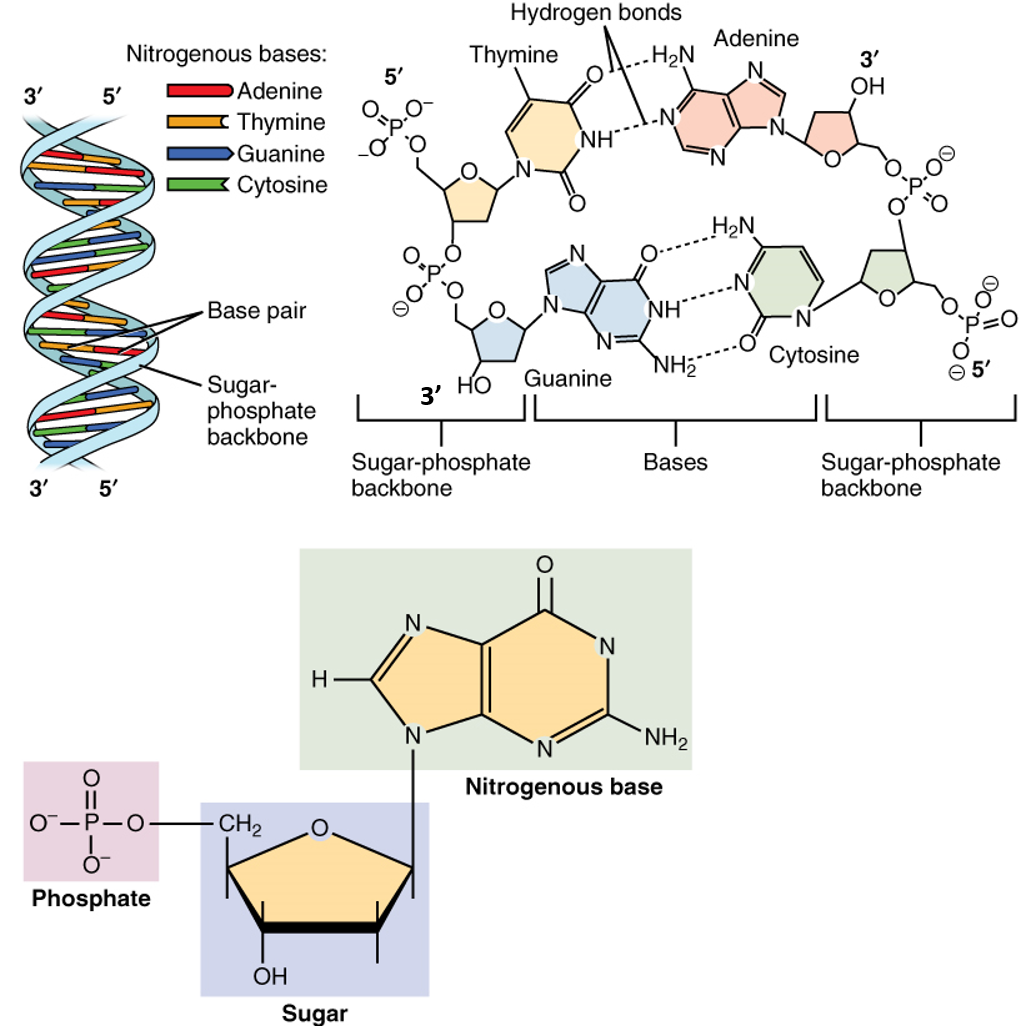
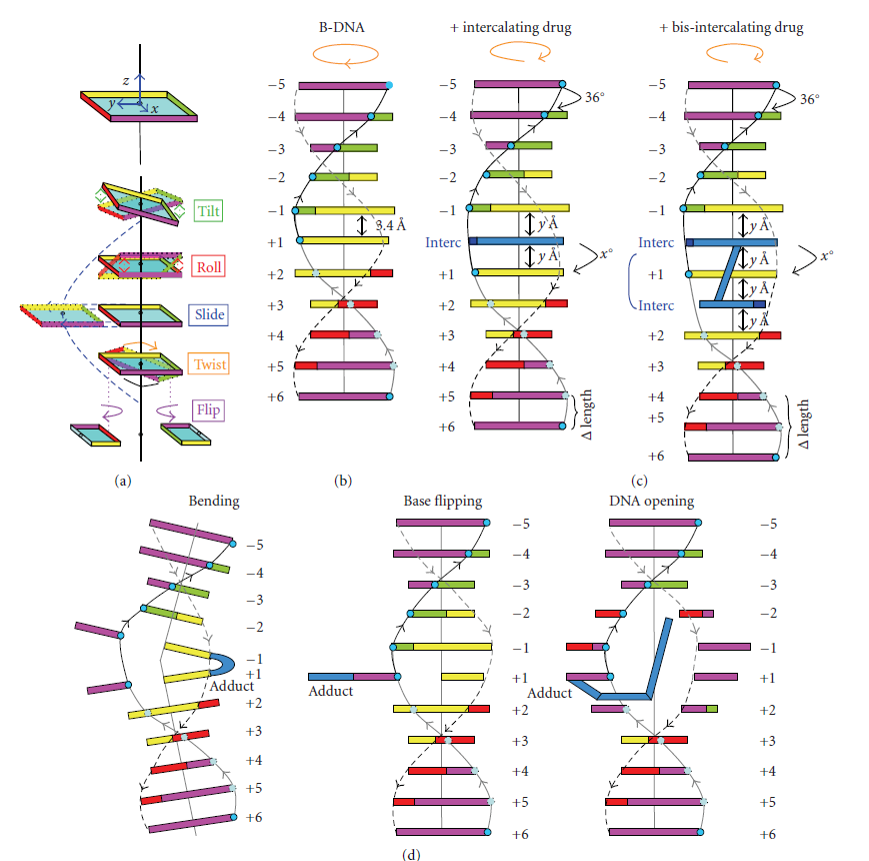
A gene is simply a length of DNA instructions stretching away to the left The assembled factors trigger the first phase of the process, reading off the information that will be needed to make the protein Everything is ready to roll three, two, one, GO!Structure of the DNA molecule A DNA molecule (deoxyribonucleine acid) is made of two chains of several thousands of linked nucleotidesEach nucleotide consists of a phosphate group, a deoxyribose and a nitrogenous base (Fig 1) The four nitrogenous bases that occur in DNA are adenine (A), guanine (G), thymine (T) and cytosine (Fig 2) Within each DNA strand, singleThat the DNA molecule is highly bent (~80 about the promoter sequence), and ~8 DNA base pairs are opened in the initially formed transcription bubble (see Fig 4)(6) Given that such largescale shifts from the equilibrium BDNA structure are thought to occur within the preinitiation complex, we sought to determine what effect mechan



Dna Structure Hs Tutorial Learn Biology




What Is Dna Structure Function Pictures Facts
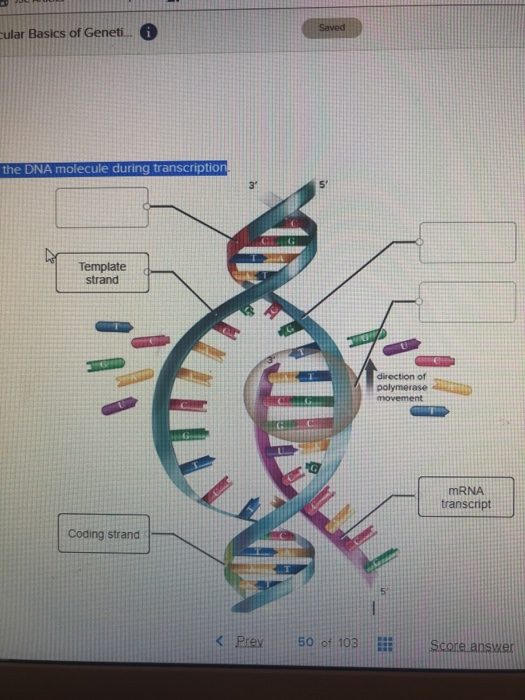
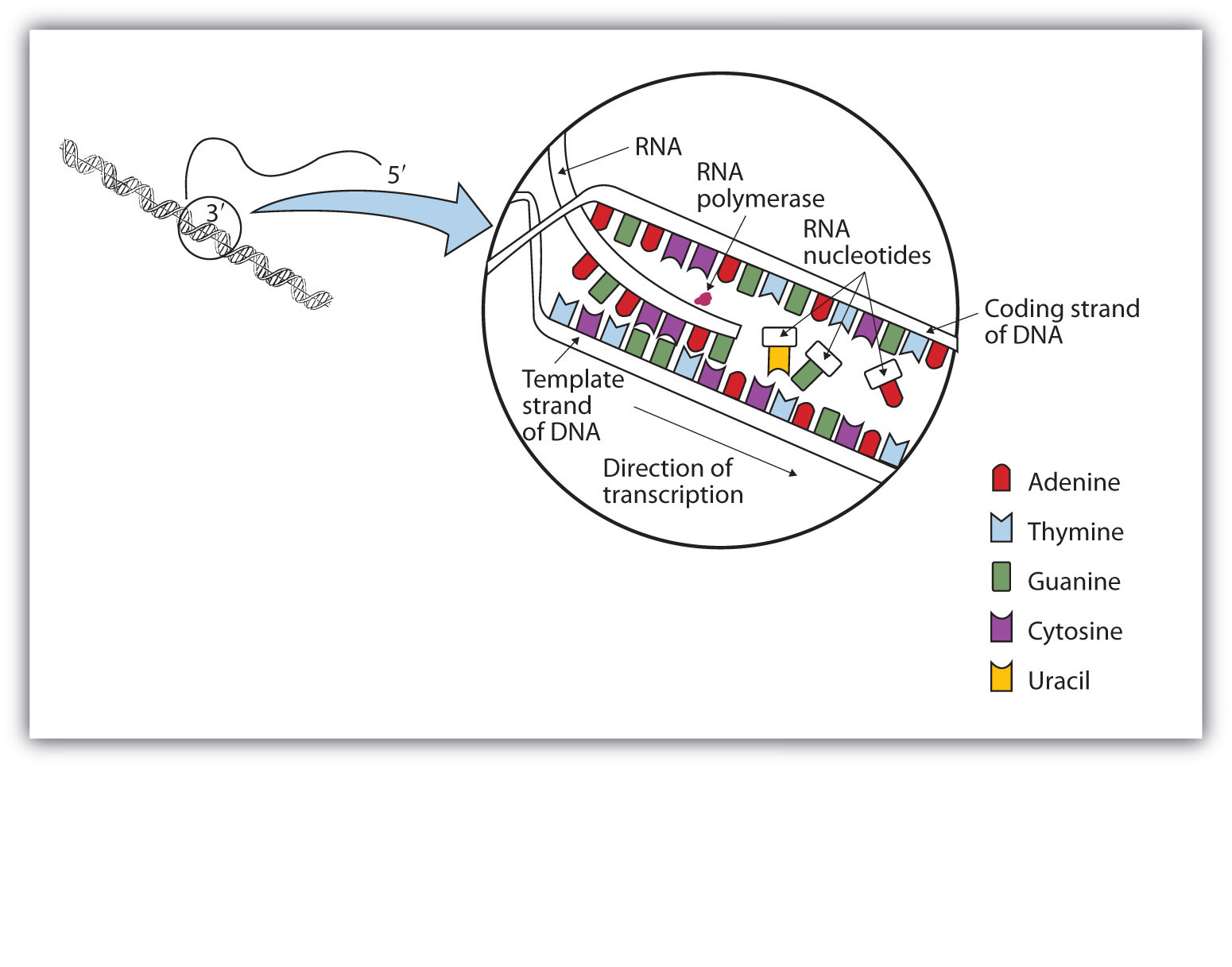
During the process of transcription, the information encoded within the DNA sequence of one or more genes is transcribed into a strand of RNA, also called an RNA transcriptThe resulting singlestranded RNA molecule, composed of ribonucleotides containing the bases adenine (A), cytosine , guanine (G), and uracil (U), acts as a mobile molecular copy of the original DNA sequenceIt must be replicated when a cell is ready to divide, and it must be "read" to produce the molecules, such as proteins, to carry out the functions of the cell For this reason, the DNA is protected and packaged in very specific waysProtein molecule Gene 1 Gene 2 Gene 3 DNA strand (template) TRANSCRIPTION Protein TRANSLATION Amino acid A C A G T U G G U U G C U A Trp Phe Gly Ser Codon 3 ʹ5 5ʹ RNA Polymerase Nontemplate




Worksheet On Dna And Rna Web Viewif The Sequence On The Right Hand Side Of The Dna Molecule Was Docx Document



Solved Ular Basics Of Geneti The Dna Molecule During Chegg Com
Students will model that DNA is the storage molecule for genetic information in the cell Students will perform transcription of DNA molecules into mRNA Students will translate the mRNA molecules into sentences that represent proteins Students will reverse the process to code a DNA molecule that will produce a given sentenceThis signals the DNA to unwind so the enzyme can ''read'' the bases in one of the DNA strands The enzyme is now ready to make a strand of mRNA with a complementary sequence of bases Does helicase unzip DNA in transcription?Step one is to build the DNA molecule, which will be much simpler than the ballandstick model I built before In this model, each base, phosphate, and sugar is one piece of plastic Each base molecule is a 25millimetrelong soft tube T is




Transcription Bubble Wikipedia




Modelling The Molecule Of Life
It first attaches to and fuses with the host cell Then the viral RNA is converted into DNA and the virus uses the host cell's machinery to replicate itself during a process called reverse transcription The new copies of HIV then leave the host cell and move on to infect other cellsThe sigma attaches to one strand of the DNA (the template strand) at a very specific location In bacteria, several sigmas exists and each one initiates the transcription of a specific sequence of DNA (or gene) Once this sigma protein attaches to the DNA molecule, it serves to guide the RNA polymerase down the template strandThis is a 38inch colorful, sturdy, flexible plastic ladder of DNA with 21 rungs the model will zip open just as the DNA molecule "unzips" for transcription of the RNA copy, or for duplication It is then activated and ready for transcription into RNA!



Chapter 4 Dna Rna And The Human Genome Chemistry




Translation Dna To Mrna To Protein Learn Science At Scitable
– EPA model of ribosome – 3Initiation, elongation,termination mRNA – Specificity of translation DNA >An indepth looks at how transcription works Initiation (promoters), elongation, and termination DNA replication and RNA transcription and translation Molecular structure of RNA Overview of transcription Stages of transcription This is the currently selected itemThe blue molecule racing along the DNA is reading the gene




File Dna Transcription Svg Wikimedia Commons




Amazon Com K Nex Education Dna Replication And Transcription Set 525 Pieces Ages 10 Science Educational Toy Toys Games
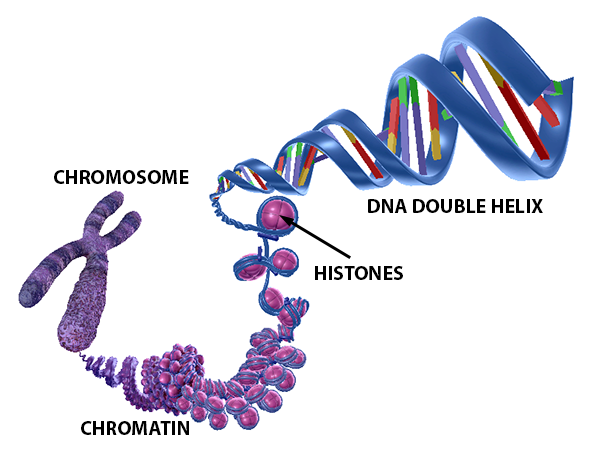
DNA the molecule that stores and encodes an organism's genetic information DNA is a double helix molecule made up of two twisted strands that are held together by hydrogen bonds between paired nucleotides The two strands are chemically oriented in opposite directions enzyme a type of protein that performs cellular activities hydrogenReplication New cells are continuously forming in the body through the process of cell division For this to happen, the DNA in a dividing cell must be copied in a process known as replication The process in which the DNA in a dividing cell is copiedThe complementary base pairing of the double helix provides a ready model for how genetic replication occurs11 Construction of a DNA molecule DNA is the genetic support of all living organisms It can be seen as a very long righthanded spiral ladder made of different constituents Each of the two peripheral chains is a succession of sugar and phosphate groups brought together by the pairing of



Dna And Rna Basics Replication Transcription And Translation




Definition Genetic Engineering Refers To The Scientific Process
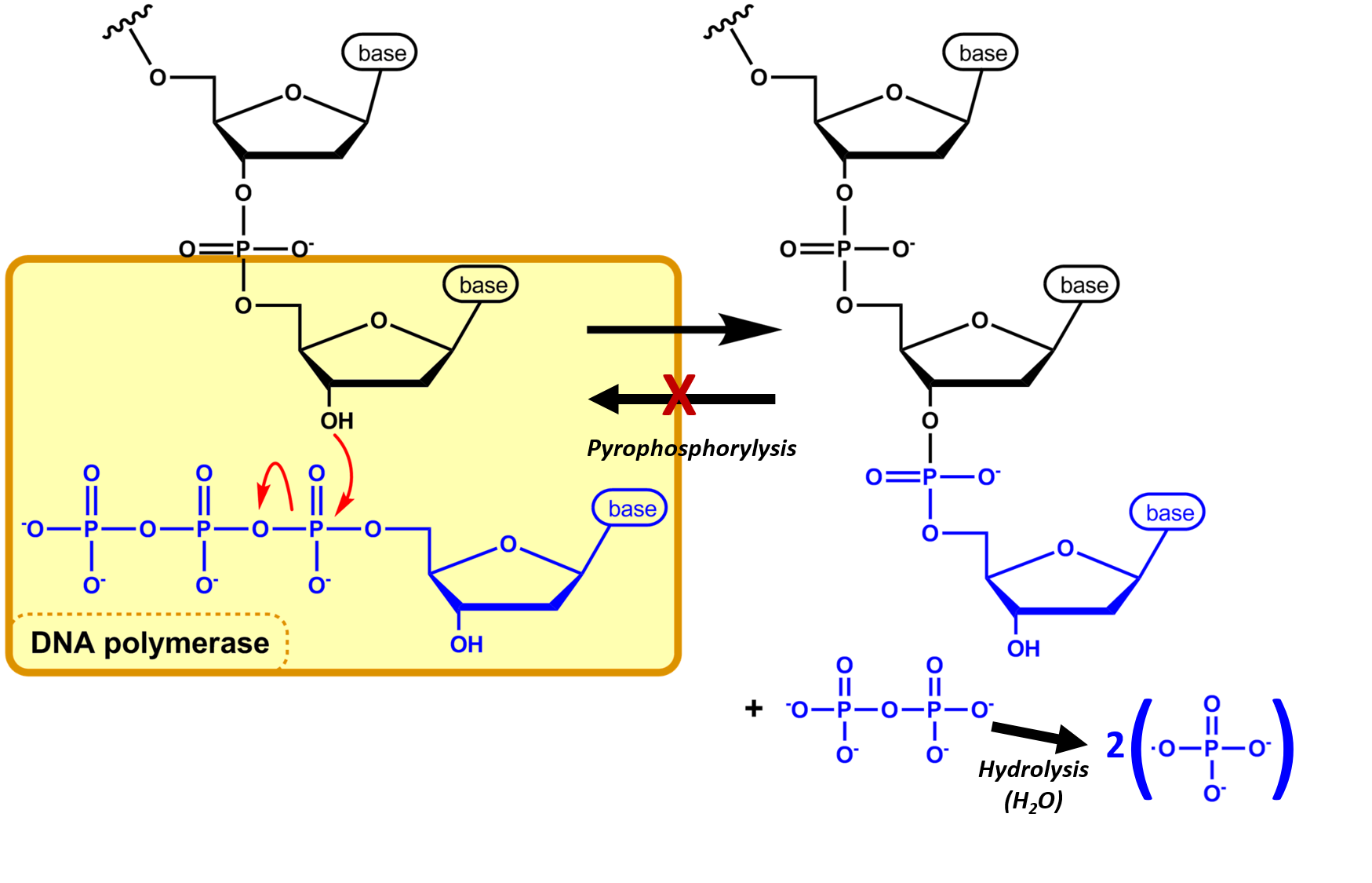
Overview of transcription Transcription is the first step in gene expression, in which information from a gene is used to construct a functional product such as a protein The goal of transcription is to make a RNA copy of a gene's DNA sequence For a proteincoding gene, the RNA copy, or transcript, carries the information needed to build aDNA is a working molecule;DNA replication consists of synthesizing another identical DNA molecule, using enzymes called polymerases, which are molecules specifically dedicated only to copy DNA Transcription, on the other hand, is the process by which a copy of messenger RNA (mRNA) is generated from the sequence of a gene in the DNA



Transcription An Overview Of Dna Transcription Article Khan Academy




Translation Dna To Mrna To Protein Learn Science At Scitable
How do you know?Making a Copy of DNA – Transcription Cells read DNA in small portions (genes) to create a protein To do this, the cell must first make a copy of the gene's code to send to the proteinbuilding machinery This process is called transcription Using the following materials, follow the steps below to see how this is done You will needAt the bubble, the Rho factor pulls the RNA transcript and the DNA template strand apart, releasing the RNA molecule and terminating the transcription process A transcription stop point sequence that is found later in the DNA causes the RNA polymerase to stop and allow the Rho factor to catch up and terminate the process



Topic 2 7 Dna Replication Transcription And Translation Amazing World Of Science With Mr Green




19 3 Replication And Expression Of Genetic Information The Basics Of General Organic And Biological Chemistry
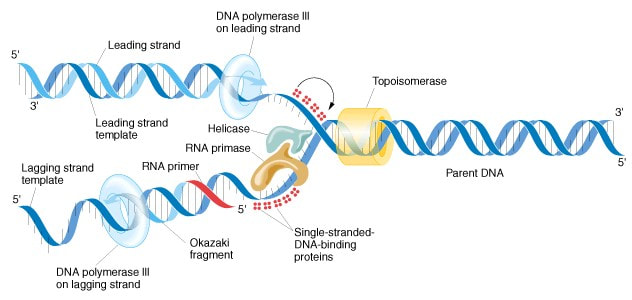
Answer After the discovery of Double helical structure of DNA by Watson and Crick, there were 3 different models regarding DNA replication proposed by scientists, those are 1 Conservative, 2 Semiconservative and 3 Dispersive 1 According toSome RNA viruses, however, called retroviruses (Figure 1018 Life Cycle of a Retrovirus), synthesize DNA in the host cell, in a process that is the reverse of the DNAtoRNA transcription that normally occurs in cells (See Figure 1010 A Schematic Diagram of RNA Transcription from a DNA Template for the transcription process)Hook/Check for Understanding Building Block Transcription 10 minutes Review the structure of DNA with students and explain to them that for this minimodel, they will be using Legos Provide student groups with a doublestranded DNA molecule that contains 12 nucleotide pairs and is made of Legos and one set of Legos to construct the RNA strand



Dna And Rna Basics Replication Transcription And Translation



Dna
Messenger RNA, DNA is its template during transcription, Carries genetic information from nucleus to cytoplasm,provides genetic information at ribosomes for translation and the codon at the A site is ready for the next tRNmino acid Put together other pieces of evidence to conclude the double helix model of DNA During DNA replicationIn DNA transcription, the DNA sequence of a gene is copied out (transcribed) in order to make a molecule of RNA It is the first step in the expression of the gene The process of DNA Transcription is done by the enzymes known as RNA polymerases In another word, DNA Transcription is a process by which the information is rewrittenDNA transcription is the process by which the genetic information contained within DNA is rewritten into messenger RNA (mRNA) by RNA polymerase This mRNA then exits the nucleus, where it acts as the basis for the translation of DNA By controlling the production of mRNA within the nucleus, the cell regulates the rate of gene expressionIn this article we will look



Dna And Rna Basics Replication Transcription And Translation



Replication And Expression Of Genetic Information
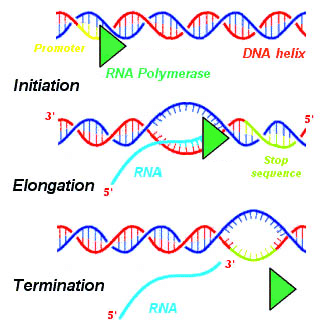
Transcription is the process by which the information in DNA is copied into messenger RNA (mRNA) for protein production Transcription begins with a bundle of factors assembling at the promoter sequence on the DNA (in red) Here, two transcription factors Duration 1 minutes, 53 seconds The Central Dogma of Molecular Biology DNA makes RNAThis is a 38inch colorful, sturdy, flexible plastic ladder of DNA with 21 rungs the model will zip open just as the DNA molecule "unzips" for transcription of the RNA copy, or for duplication It is then activated and ready for transcription into RNA!The blue molecule racing along the DNA is reading the gene




Solved Tein Synthesis Activity 2 Transcription When Chegg Com




Transcription Cie As Biology Revision Notes
The enzyme DNA helicase breaks the hydrogen bonds between the bases in a specific region of the DNA moleculeThe "Dynamic DNA Model" is now available!Answer (1 of 6) DNA is book which can be read into 2 different states one is transcription and translation In transcription process double stranded DNA gives birth to single stranded RNA molecule In transcription process the DNA molecules acted as stock where many RNA branches extending out ,




Dna Transcription Learn Science At Scitable




Rules Governing The Behaviour Of Rna Polymerase As An Example Swarm Download Table
The DNA molecule unzips in both directions •Step 2 DNA Polymerase (enzyme) inserts and –Newly made strands coil back up and are ready for use original strand new strand Two molecules of DNA DNA is unzipping •RNA is a link between2 Prepare your other supplies Gather string and toothpicks to be used in creating the model The string should be cut to be about 1 foot (30 cm) long, although you can make it longer or shorter based on your preferred size of DNA model Use 2 pieces of string that are the same length to make the double helixDuring transcription, the DNA of a gene serves as a template for complementary basepairing, and an enzyme called RNA polymerase II catalyzes the formation of a



Chapter 4 Dna Rna And The Human Genome Chemistry



23 7 Dna Replication The Double Helix And Protein Synthesis Chemistry Libretexts
A gene is simply a length of DNA instructions stretching away to the left The assembled factors trigger the first phase of the process, reading off the information that will be needed to make the protein Everything is ready to roll three, two, one, GO!Full Description Add To CartThe DNAdependent RNA polymerase binds to the promoter and catalyses the polymerization in the 5' to 3' direction on the template strand Once it reaches the terminator sequence, the process terminates and the newly synthesised RNA strand is released Transcription Unit is a stretch of a DNA transcribed into an RNA molecule




Protein Biosynthesis Wikipedia



Chapter 9 Dna Structure Protein Synthesis And Gmo S Human Biology




From Gene To Phenotype Part 2 Dna Molecule




The Structure Of Dna By Ron Vale Genetics The Structure Of Dna




Lesson Explainer Transcription Nagwa



Chapter 4 Dna Rna And The Human Genome Chemistry




Scientific Model Dna And Rna Transcription And Translation Vector Isolated On White Stock Illustration Download Image Now Istock



1



Chapter 4 Dna Rna And The Human Genome Chemistry



Activity A Get The Gizmo Ready G G Build A Dna If Necessary Click Reset To Start The Building At Molecule Process C G Question What Is The Course Hero




Nucleic Acid Encoded Mab Timeline Antibodies Are Identified From Download Scientific Diagram




Translation Transcription Quiz Review Why Does Transcription Take Place A To Make A Dna Molecule B To Make Amino Acids From Mrna C To Form Proteins Ppt Download




Pdf Transcription And Translation




Transcription Bubble Wikipedia
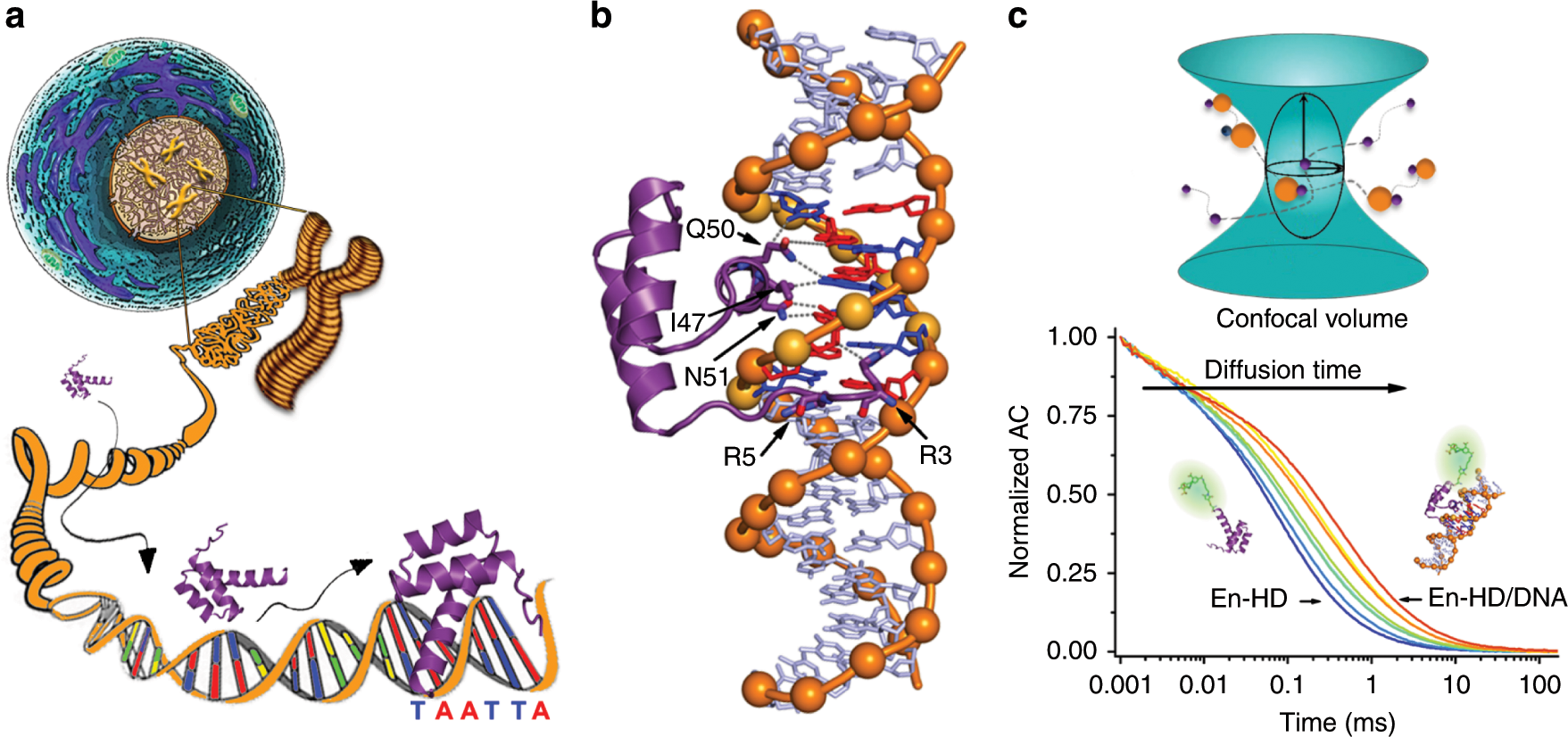



Eukaryotic Transcription Factors Can Track And Control Their Target Genes Using Dna Antennas Nature Communications




The Structure Of Dna By Ron Vale Genetics The Structure Of Dna




A Science Odyssey Dna Workshop Text Version



Topic 2 7 Dna Replication Transcription And Translation Amazing World Of Science With Mr Green
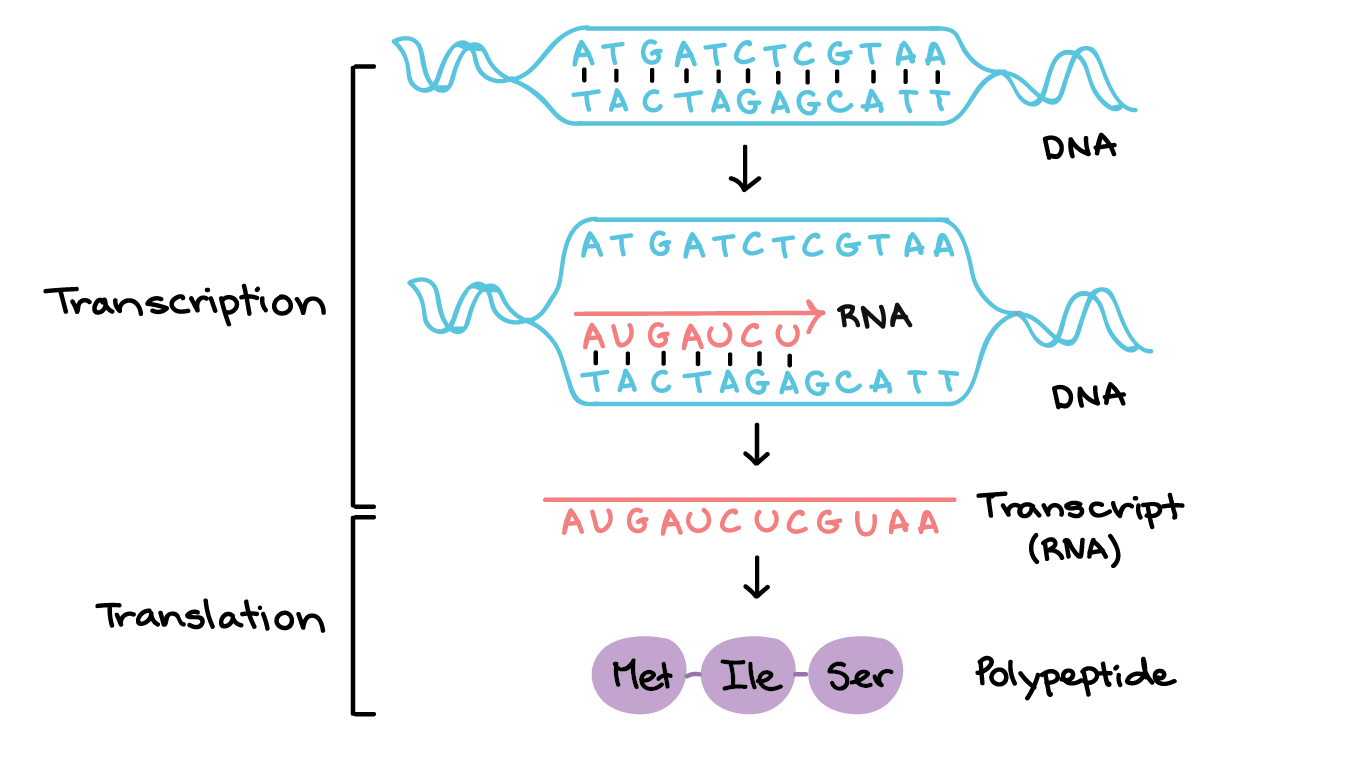



Transcription An Overview Of Dna Transcription Article Khan Academy



1




The Dna Structure Salient Features Dna Helix Packaging Videos Q A




Structural Insights Into Transcription Initiation From De Novo Rna Synthesis To Transitioning Into Elongation Sciencedirect
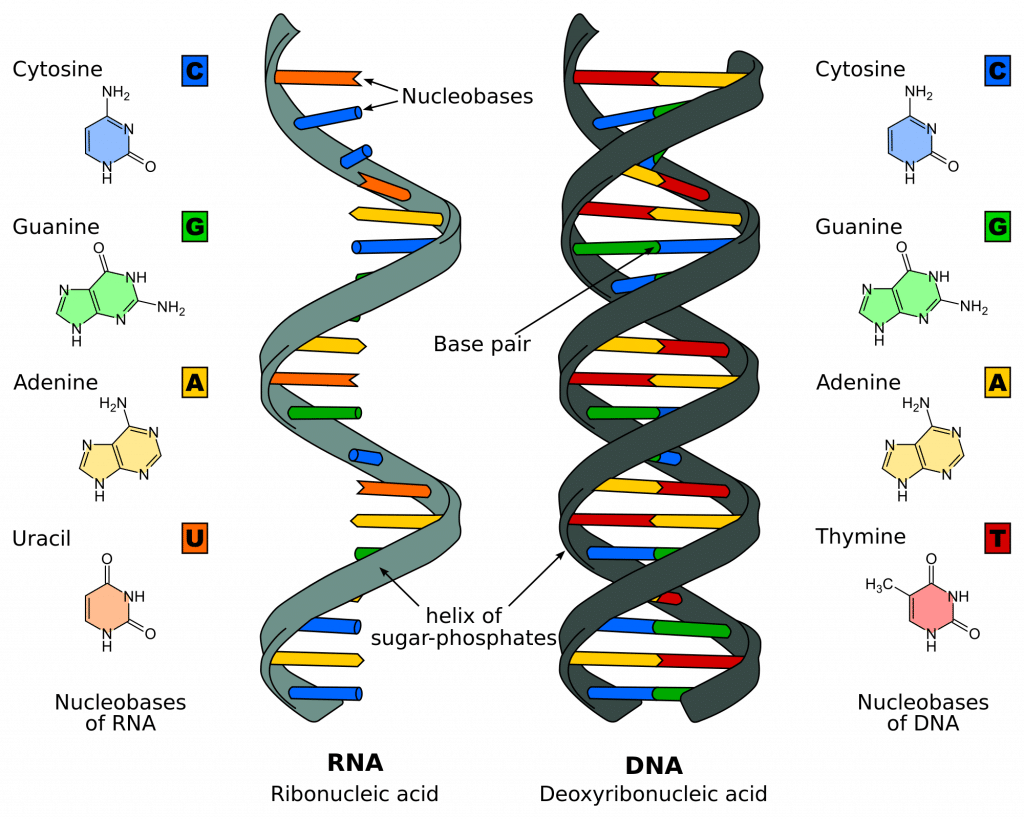



Transcription Of Dna Stages Processing Teachmephysiology




Dna Transcription And Mrna Processing Video Khan Academy




Transcription Definition Steps Biology Britannica




The Dna Structure Salient Features Dna Helix Packaging Videos Q A



9 2 Dna Replication Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition
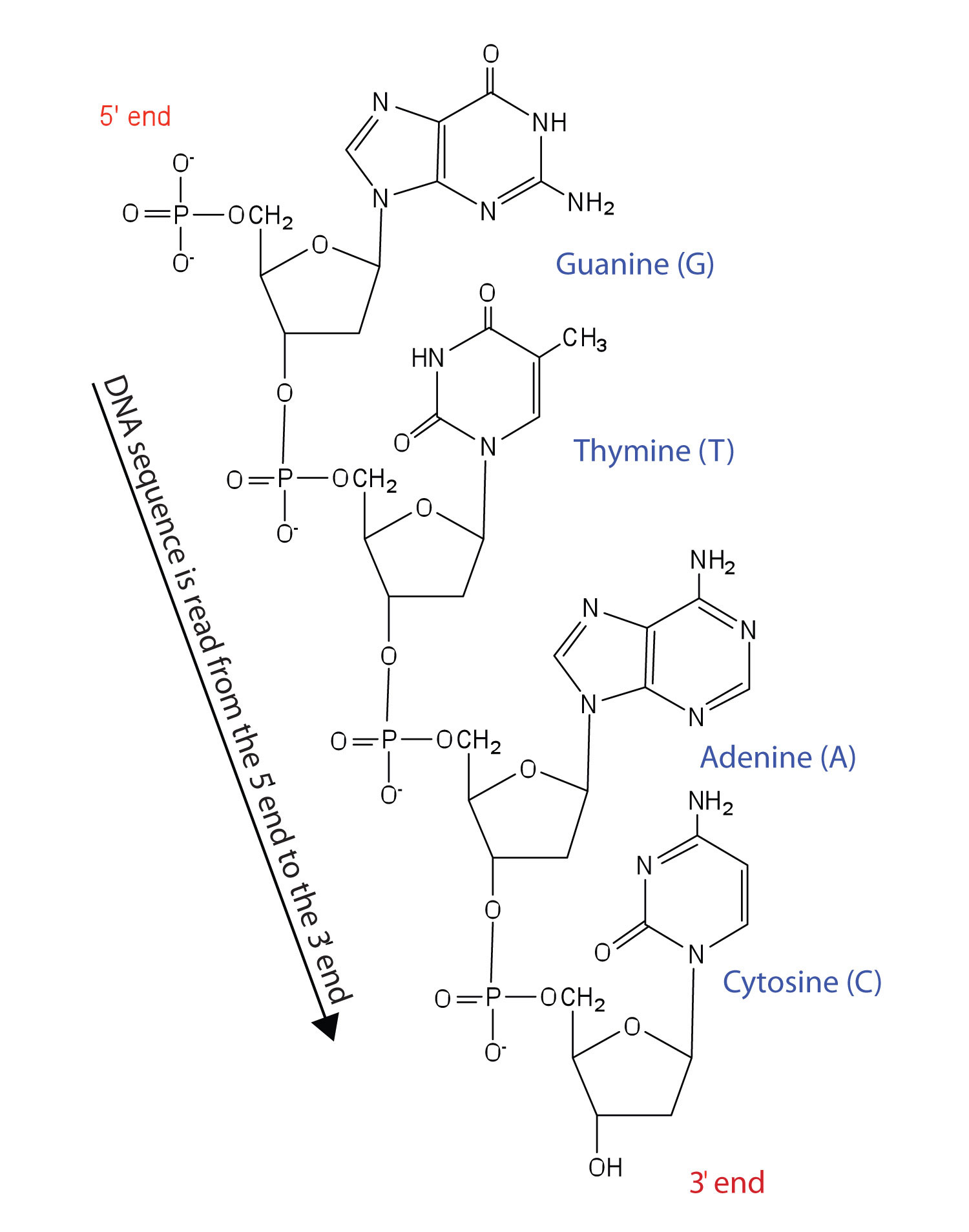



23 7 Dna Replication The Double Helix And Protein Synthesis Chemistry Libretexts




Transcription Dna Molecular Model Kit Carolina Com




Worksheet On Dna And Rna Nbsp Web Viewname Date Worksheet On Dna Rna And Protein Synthesis Docx Document




The Structure Of Dna By Ron Vale Genetics The Structure Of Dna
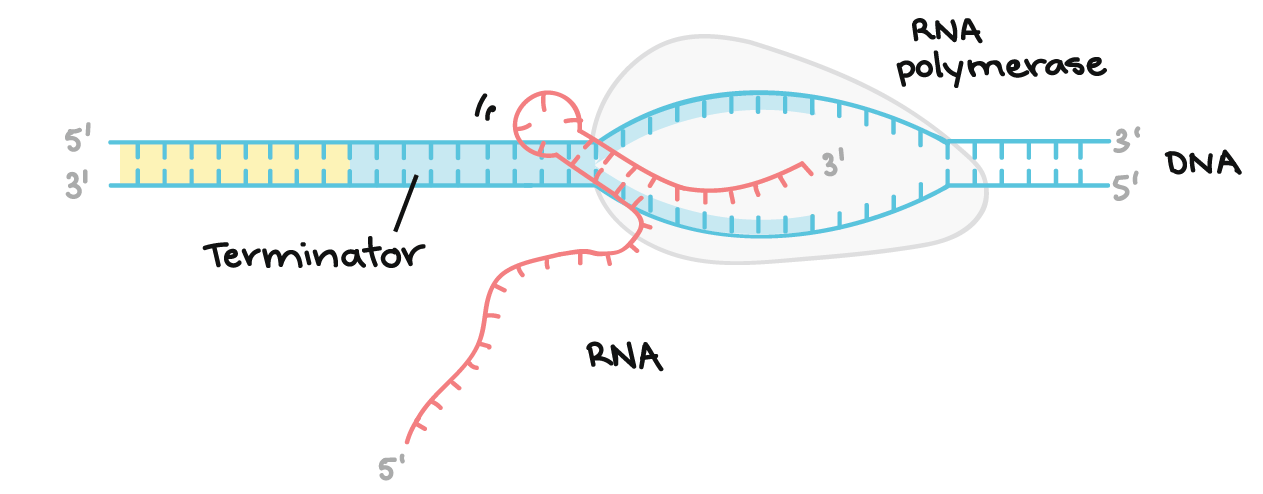



Transcription An Overview Of Dna Transcription Article Khan Academy
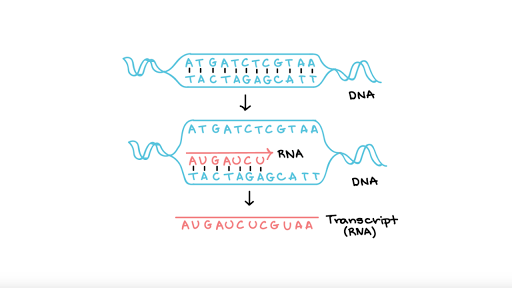



Transcription An Overview Of Dna Transcription Article Khan Academy




Flow Of Genetic Information Kit C
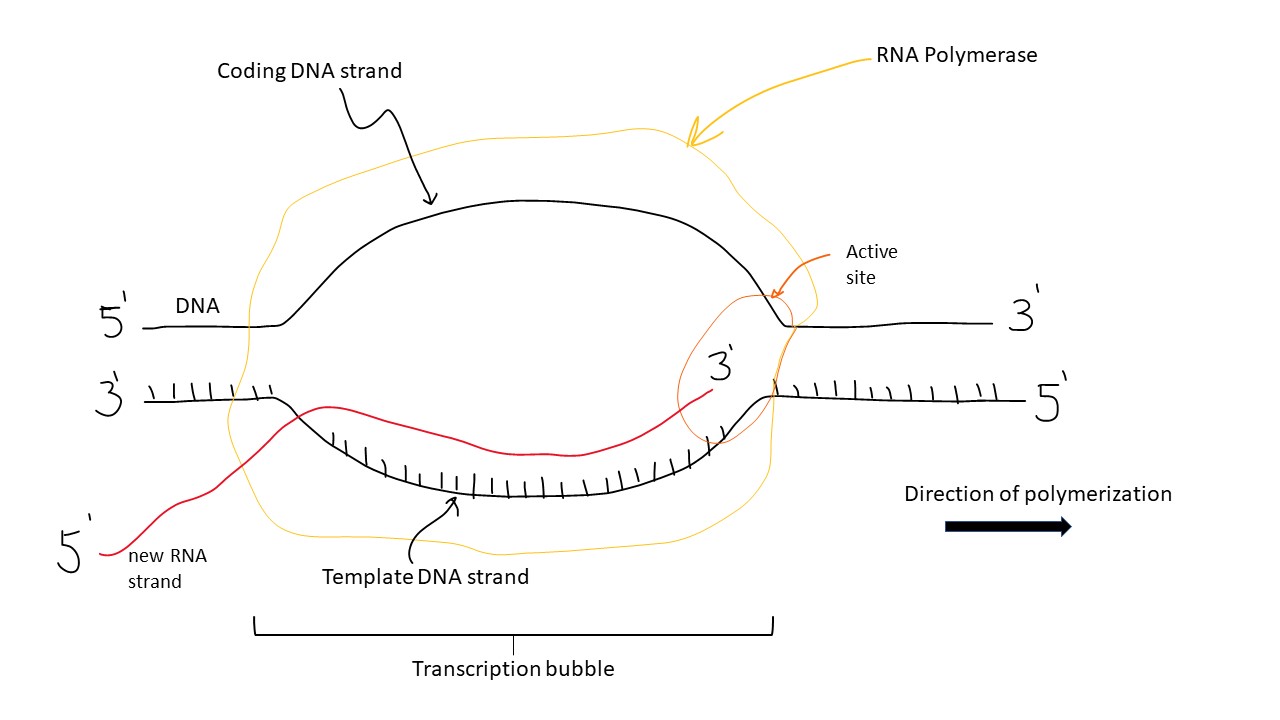



Transcription Bubble Wikipedia




Translation Dna To Mrna To Protein Learn Science At Scitable
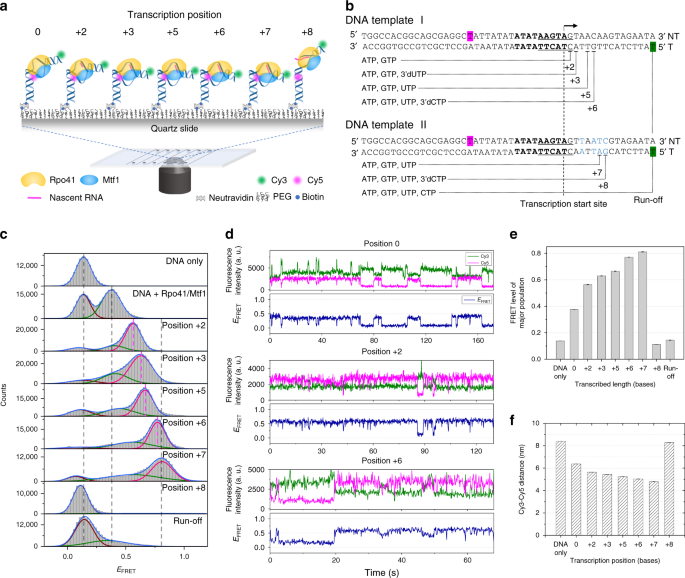



The Dynamic Landscape Of Transcription Initiation In Yeast Mitochondria Nature Communications




41 Dna Transcription Illustrations Clip Art Istock



Solved Activity B Get The Gizmo Ready Dna Be Sure The Hint Reads Quot The Dna Molecule Is Complete Quot Replication If Not Click Reset And B Course Hero




Synthetic Biology Protein Synthesis Ppt Download




Flow Of Genetic Information Kit C




Chapter 12 And 13 Transcription And Translation Lecture 12 October 28 03 What S Due Ch6 And Ch10 Problem Set If You Haven T All Ready Turned It In Ppt Download




Flow Of Genetic Information Kit C
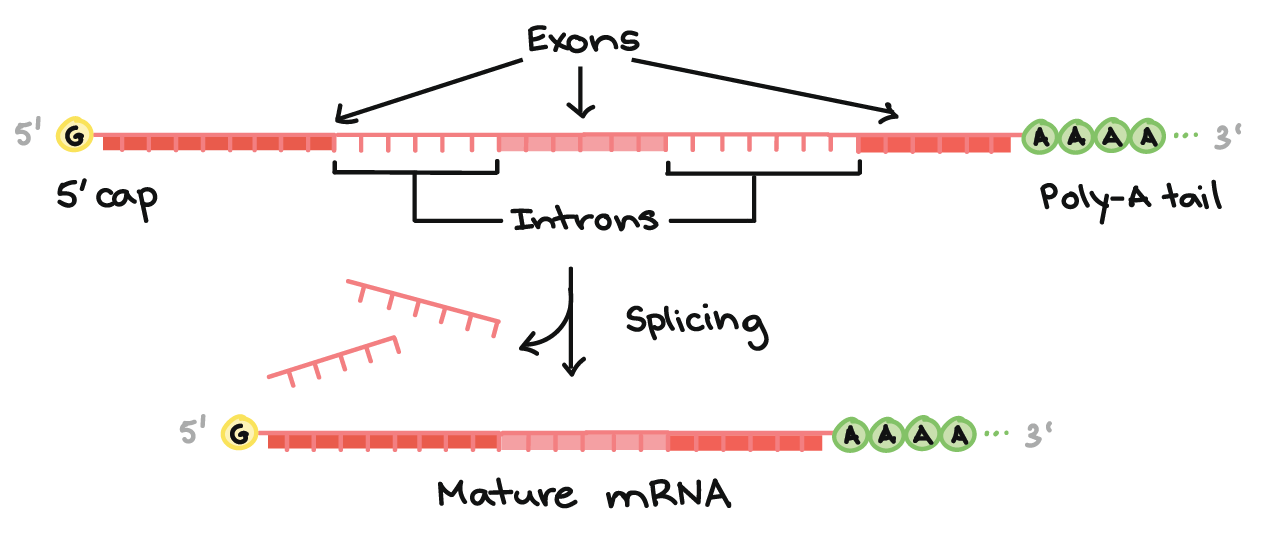



Transcription An Overview Of Dna Transcription Article Khan Academy




Modeling Transcription And Translation




How Helicase Unwinds The Dna Double Helix In Preparation For Replication Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



Topic 2 7 Dna Replication Transcription And Translation Amazing World Of Science With Mr Green




2 Basic Overview Of Transcription And Translation A Basic Gene Download Scientific Diagram




Transcription Definition Steps Biology Britannica




Dna Replication Transcription And Translation Stock Illustration Download Image Now Istock
/transcription-factor-and-ribosomal-rna-185759536-5be335b9c9e77c005147e9ec.jpg)



Steps Of Transcription From Dna To Rna




41 Dna Transcription Illustrations Clip Art Istock




41 Dna Transcription Illustrations Clip Art Istock
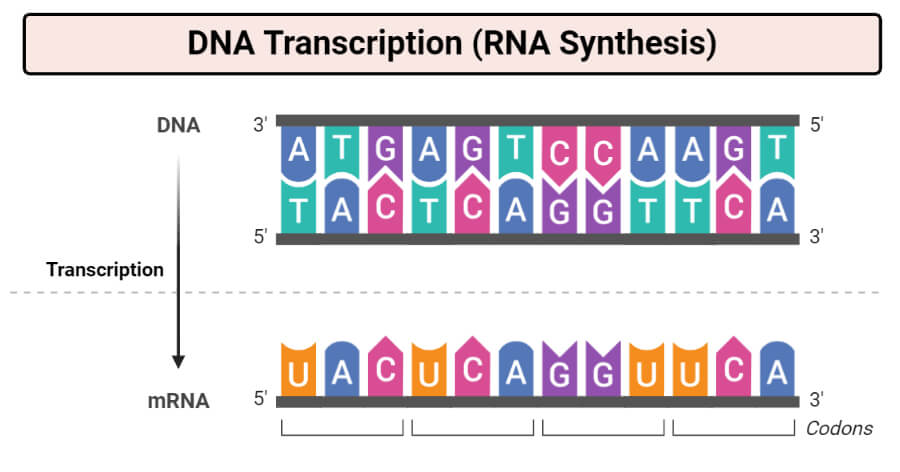



Dna Transcription Rna Synthesis Article Diagrams And Video
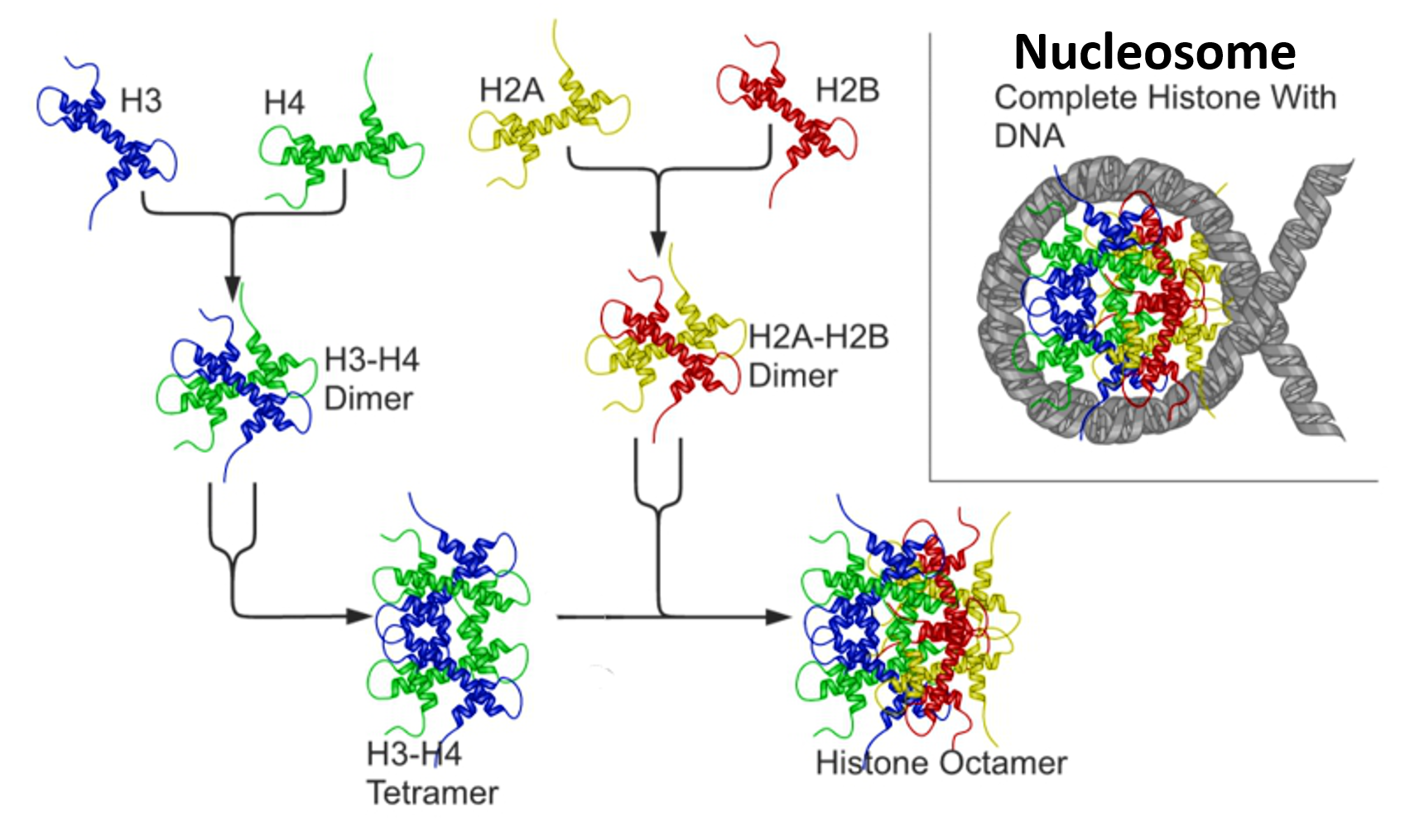



Chapter 4 Dna Rna And The Human Genome Chemistry




Dna Transcription Basic Youtube



Botany Online Molecular Genetics Transcription
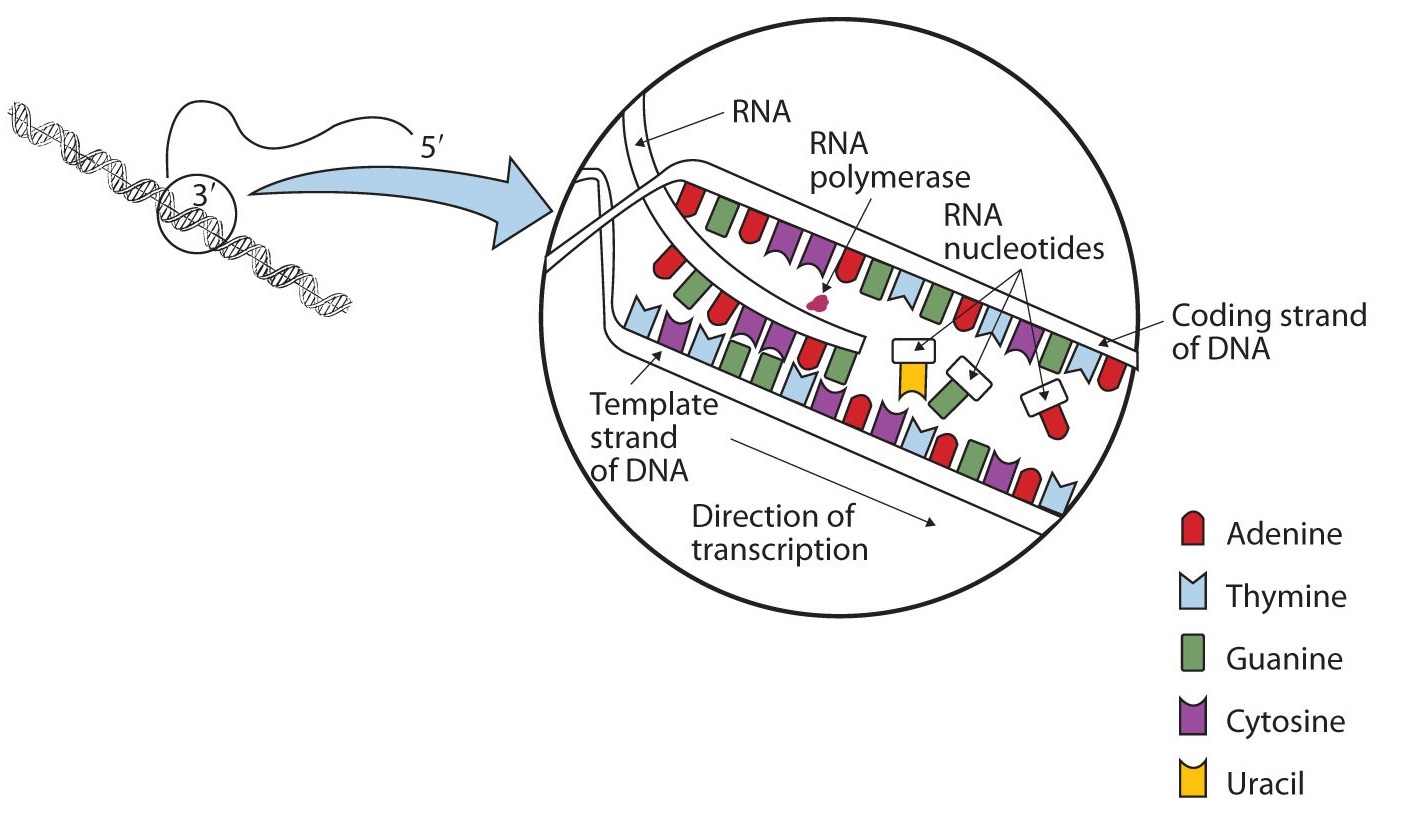



8 3 Replication And Expression Of Genetic Information Chemistry Libretexts




Solved Lab Exercise 2 Replication Transcription And Chegg Com




Dna Replication And Rna Transcription And Translation Video Khan Academy



9 1 The Structure Of Dna Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition




Protein Synthesis Anatomy And Physiology I




Chapter 3 Gene Expression Transcription Synthesis Of Proteins Translation And Regulation Of Gene Expression Flashcards Quizlet




Dna Structure And Replication Crash Course Biology 10 Youtube
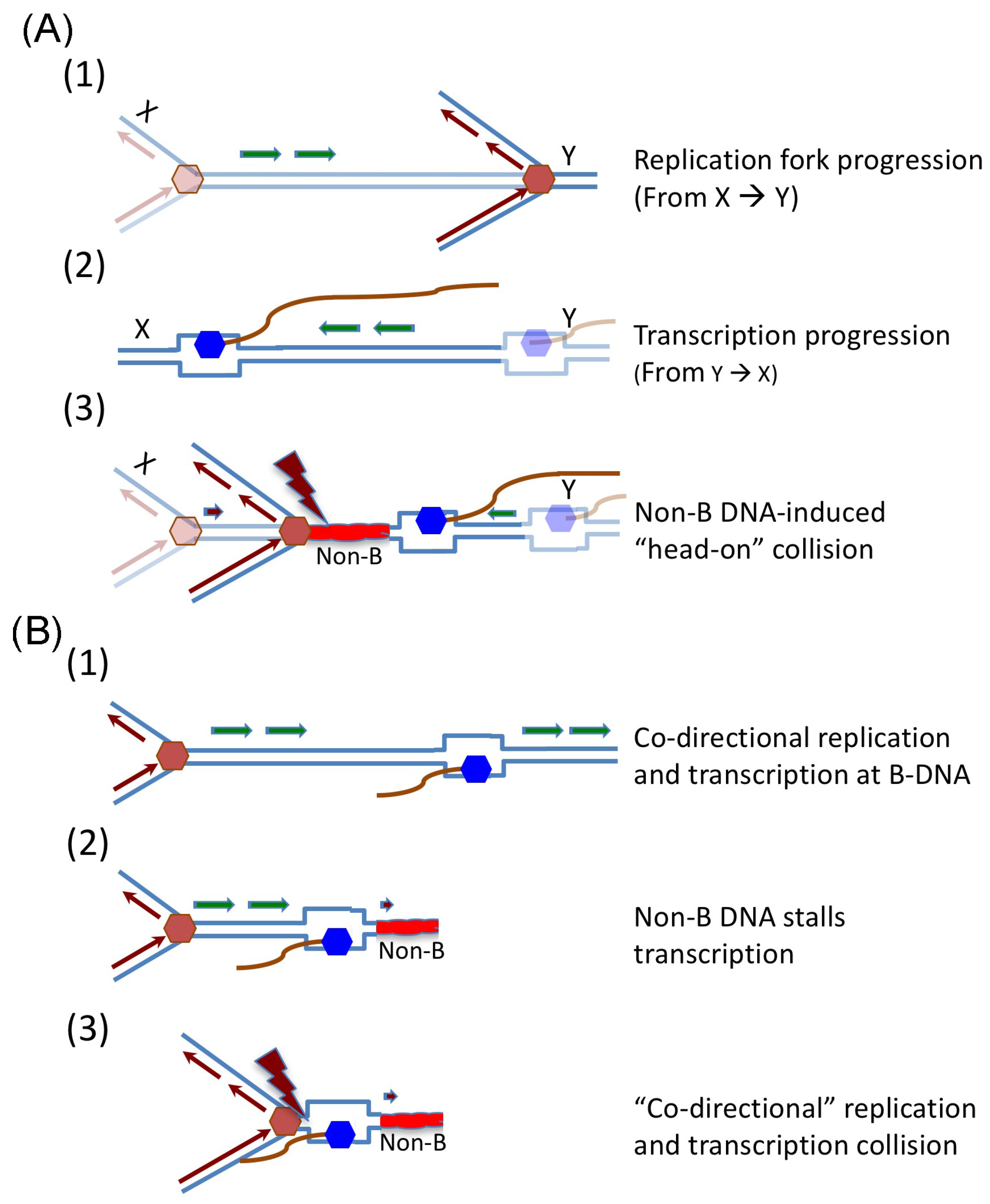



Genes Free Full Text Effects Of Replication And Transcription On Dna Structure Related Genetic Instability Html
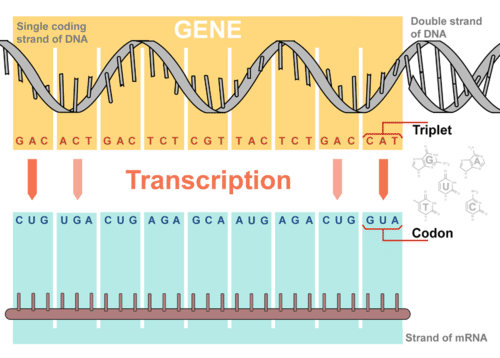



Steps Of Genetic Transcription Biology For Majors I
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/nucleotides-5c253d8cc9e77c0001d9b089.jpg)



Steps Of Transcription From Dna To Rna
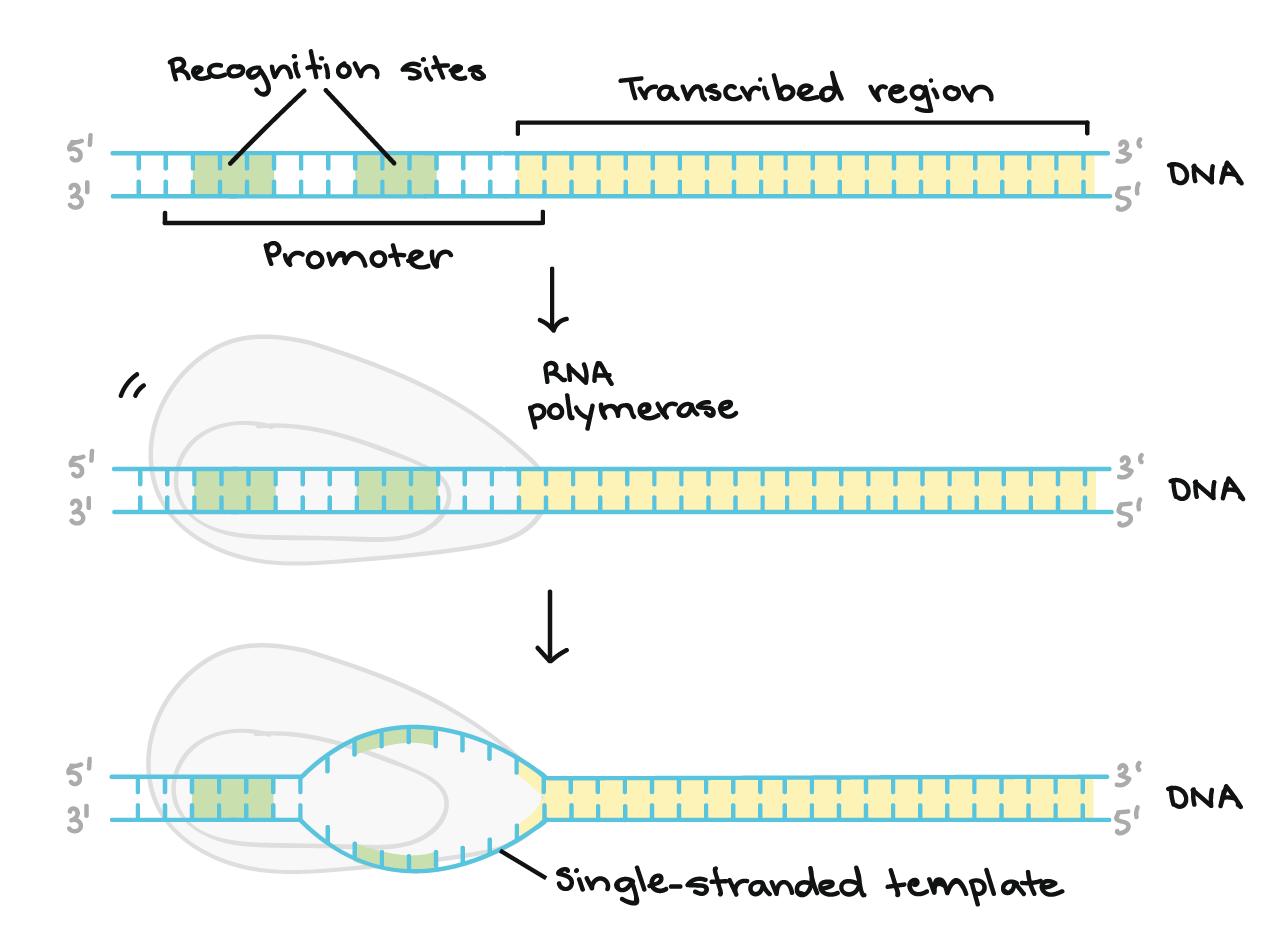



Transcription An Overview Of Dna Transcription Article Khan Academy
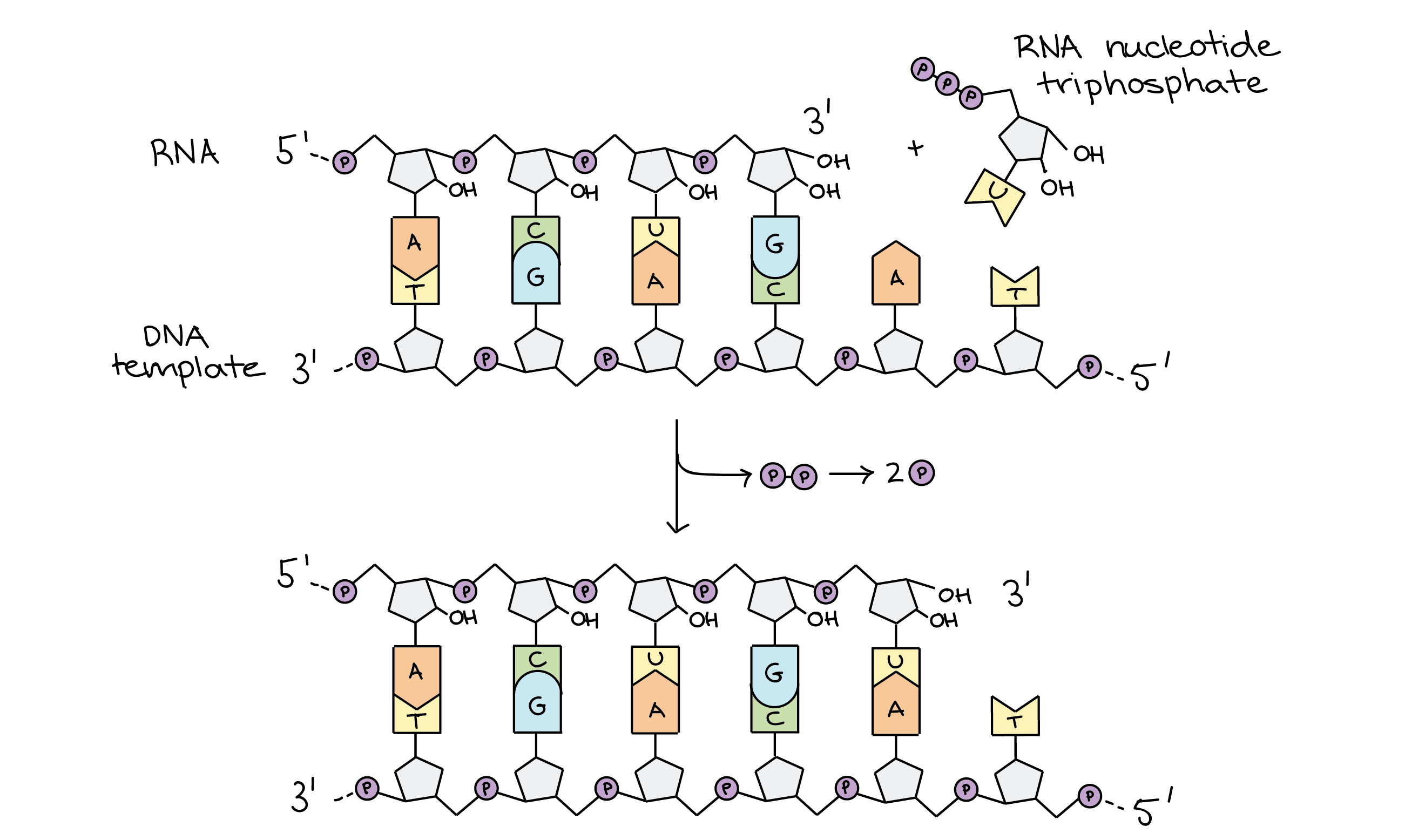



Stages Of Transcription Initiation Elongation Termination Article Khan Academy



1



Solved 1 Give The Names Of The Areas Of Dna Where Chegg Com




Pdf Dna Structure And Function



9 1 The Structure Of Dna Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition
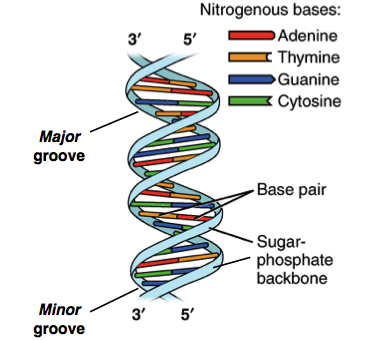



Dna Structure And Replication Review Article Khan Academy
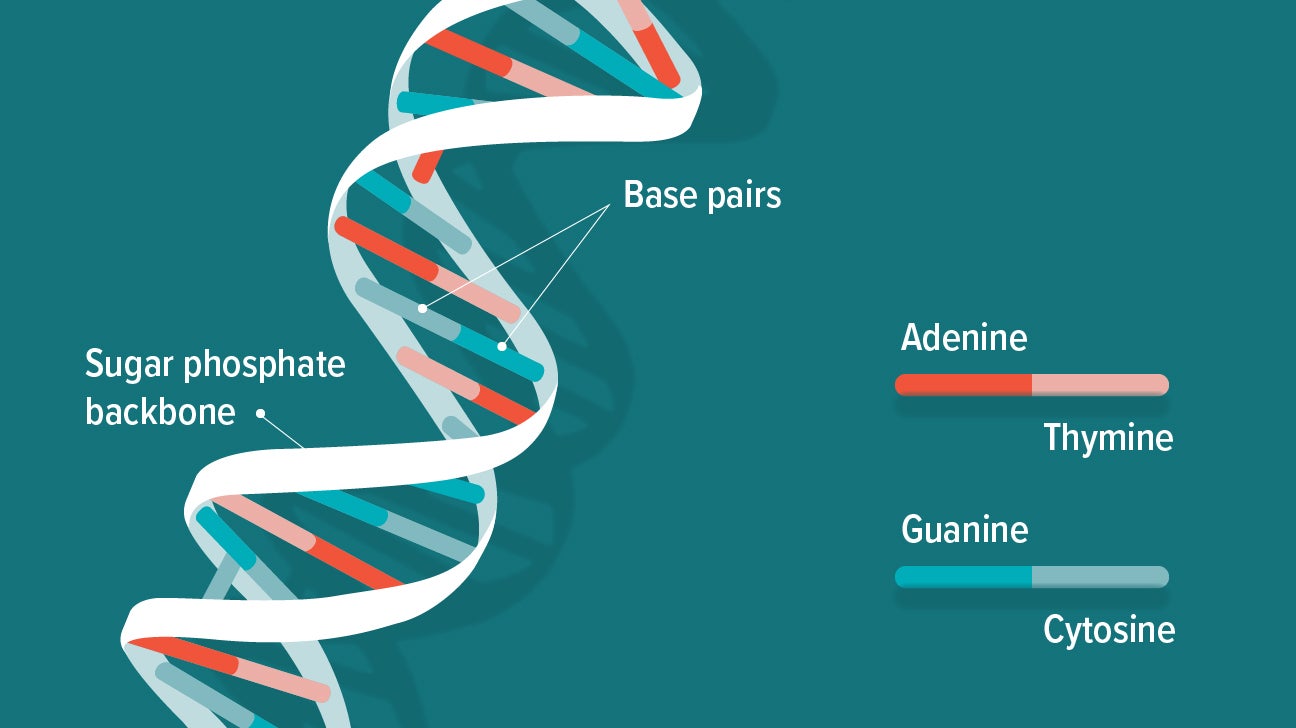



What Is Dna Structure Function Pictures Facts



Dna Structure And Replication


