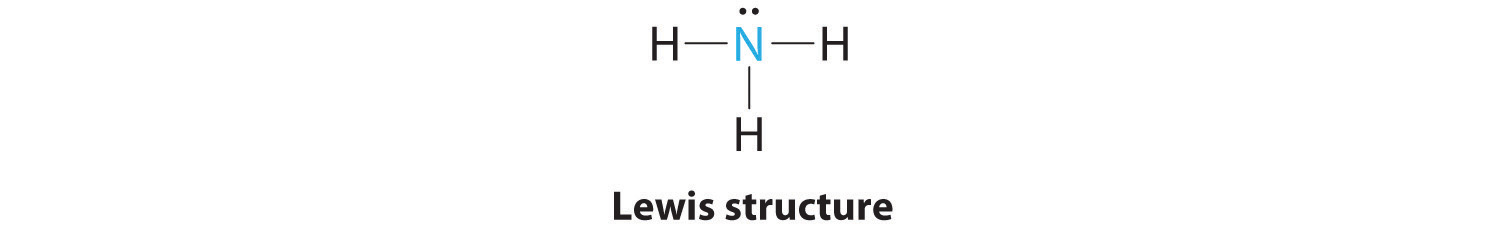
Examples O 2, N 2, C 2 H 4;What is the molecular shape around the nitrogen atom in the structure shown below?Molecular shapes In Chapter 8 we used Lewis structures to account for the formulas of covalent compounds (Section 85) Lewis structures, however, do not indicate the shapes of molecules;

Vsepr Theory
In questions 3 and 4 provide the name of the molecular shape for each lewis structure
In questions 3 and 4 provide the name of the molecular shape for each lewis structure-Advanced Steps If you have extra electrons after the above steps add them to the central atom Note elements in the Period Three (usually S, P, or Xe) can have more than eight valence electrons Examples ClF 3, SF 4,XeH 4;Draw the Lewis structure for SiH4 and give the following a the molecular shape b the electron pair geometry at the central atom c the hybridization of the central atom View Answer



3 Draw A Lewis Structure For Co2 Draw All If More Than One Resonance Structure Is Possible 4 Predict The Molecu Homeworklib
The resulting Lewis electron dot structure displays a triple bond connecting a carbon and an oxygen atom, each holding a lone pair of electrons Solved Examples Problem1 In terms of electron dot formulas, define the electron structure of the carbonate ion CO 3 2CH 2 O (16) For each of the three carbons in this molecule, provide the requestedQuestion 5 (continued) (d) Xenon can react with oxygen and fluorine to form compounds such as XeO 3 and XeF 4 In the boxes provided, draw the complete Lewis electrondot diagram for each of the molecules represented below XeO 3 XeF 4 One point is earned for each correct Lewis electrondot diagram Omission of lone pairs of
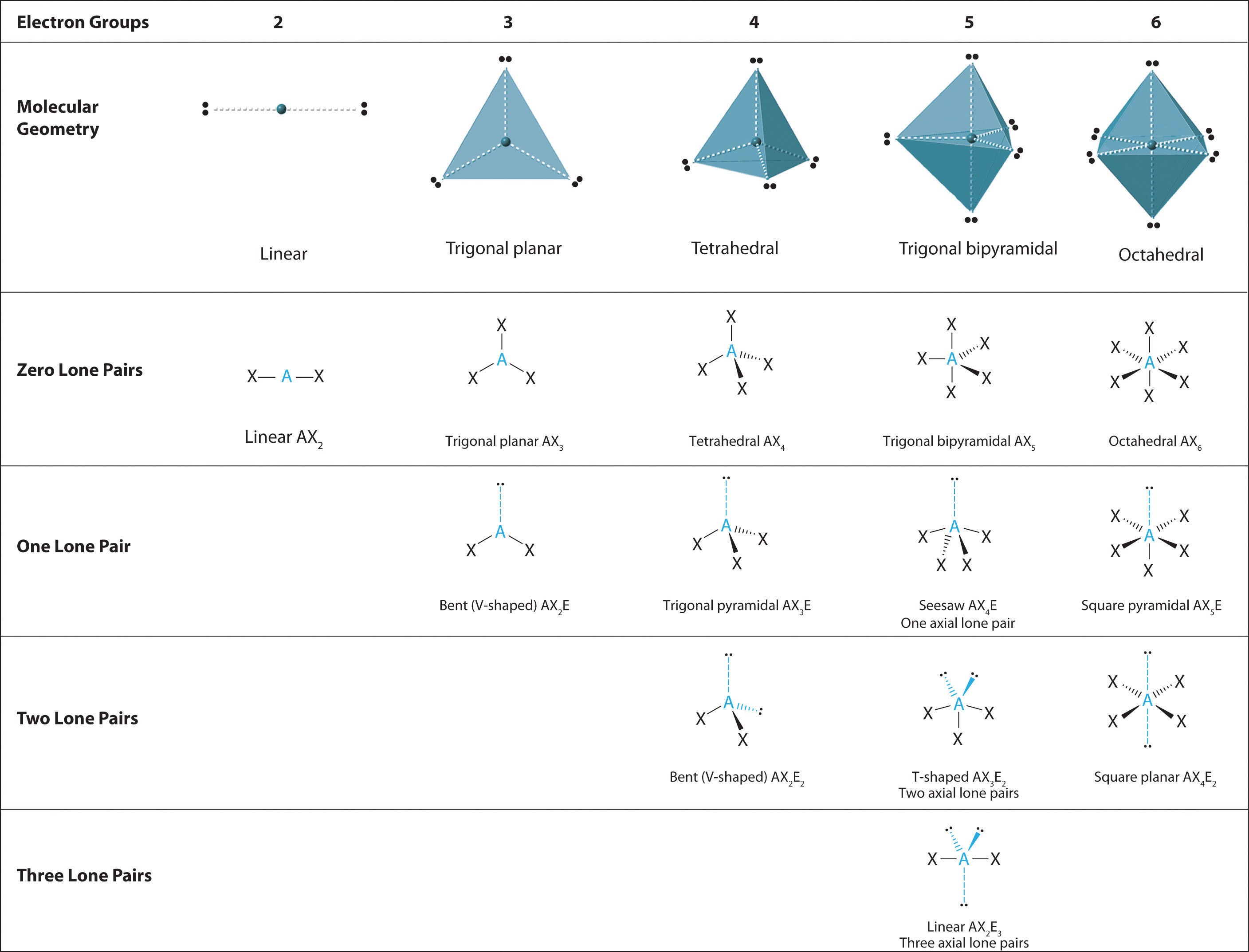
Many of the physical and chemical properties of a molecule or ion are determined by its threedimensional shape (or molecular geometry) Lewis structures are very useful in predicting the geometry of a molecule or ion The valence shell electronpair repulsion theory (abbreviated VSEPR) is commonly used to predict molecular geometryThe true shape of a molecule is important because it determines many physical and chemical properties for the substance In this activity you will learn how to predict molecular shapes 3D Molecular Shape Model 1 — Lewis Structures Lewis I H 2 CO NH Lone pair — Molecular Geometry H CO 3 electron domain (3 bonding, 0 nonbonding) BeFThe methane molecule, CH 4, can be used to illustrate the procedure for predicting molecular shape The Lewis structure of this molecule ascribes four bonding electron pairs to the carbon atom (Figure 8) These pairs repel one another, and their separation is maximized if they adopt a tetrahedral disposition around the central carbon atom
Advanced Steps If you have extra electrons after the above steps add them to the central atom Note elements in the Period Three (usually S, P, or Xe) can have more than eight valence electrons Examples ClF 3, SF 4,XeH 4;H2O BeH2 The oxygen and carbon atoms each have an octet of electrons in their valence shellsFor the compound {eq}PO_4^{3} {/eq}, identify the following name, number of valence electrons, number of electron domains, parent geometry, molecular geometry, hybridization, number of sigma
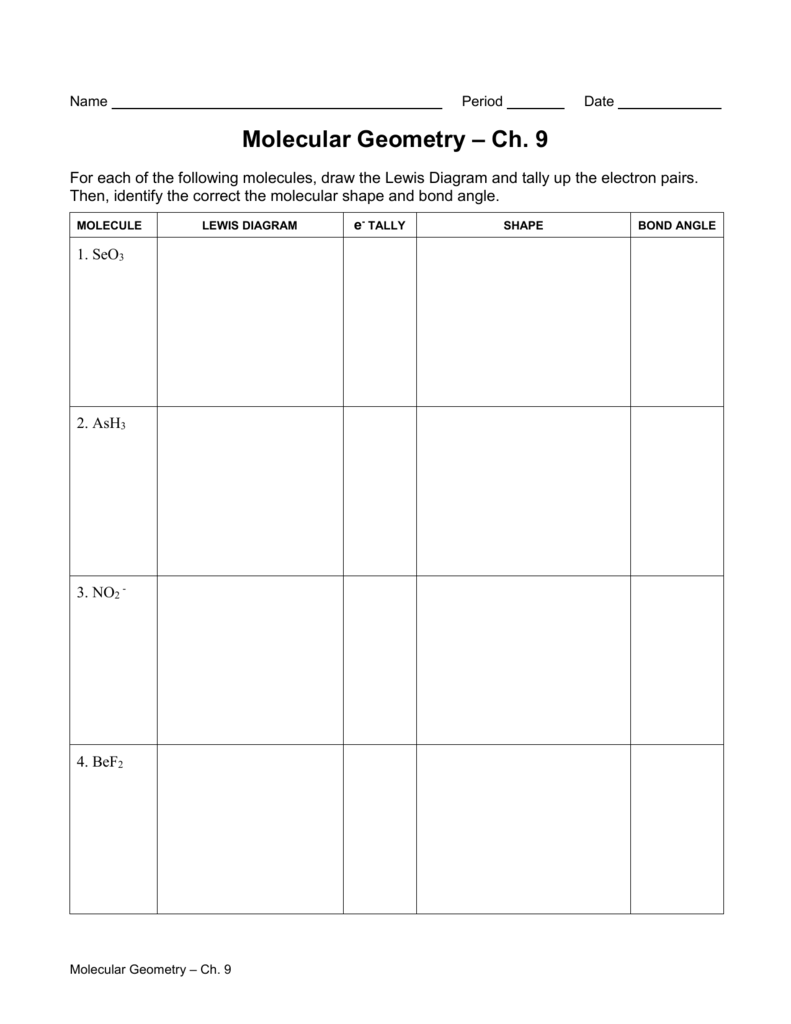


Molecular Geometry Worksheet



Types Of Molecular Shapes 3 Points Identify The Following Molecular Shapes 05 Course Hero
Video Drawing the Lewis Structure for PO 4 3 For the PO4 3 Lewis structure use the periodic table to find the total number of valence electrons for the PO4 3 molecule Once we know how many valence electrons there are in PO4 3 we can distribute them around the central atom with the goal of filling the outer shells of each atom335 Practice Bonding in Matter c What shape would SeH 2 have?We can use the following notations when examining a Lewis structure of a molecule A = central atom X = peripheral atoms E = nonbonding electron pairs of the central atom #AX_2# = linear molecule #AX_3# = trigonal planar #AX_3E# = trigonal pyrimidal #AX_2E_2# = bent #AX_4# = tetrahedral molecule Here are some examples



Drag Each Label To The Correct Location Identify The Molecular Shape Of Each Lewis Brainly Com


Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory Vsepr
Ownership of Intellectual Property Except as expressly provided herein, no other license is granted hereby and GGA retains all rights, title and interest in and to the Software and all derivative works thereof, including, without limitation, any and all intellectual property rights thereinChapter 6 – Molecular Structure Introduction A method for constructing Lewis structures of simple molecules and ions was presented in Chapter 5In this chapter, we show how to use Lewis structures to determine the structural and bonding properties of molecules and ions with covalent bondsDraw the molecule (1 point) Question 8 Ionic and Covalent Compounds (5 points) Identify each of the following as a covalent compound or ionic compound Then provide either the formula for compounds identified by name or the name for those identified by formula (1 point each) a


7 E Chemical Bonding And Molecular Geometry Exercises Chemistry Libretexts



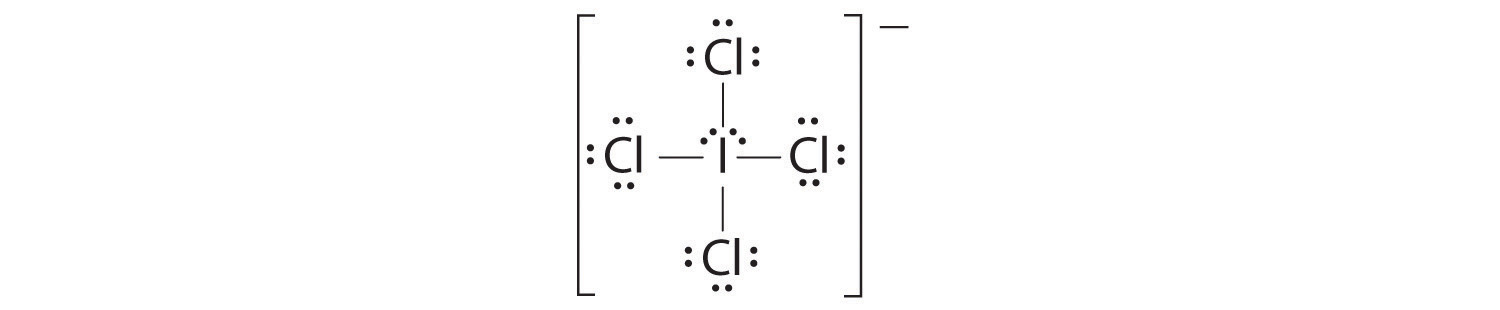
For The Ion I3 1 Draw A Lewis Structure 2 State The Geometry Of Molecule If It Has More Than One Central Atom G Homeworklib
Central Atom(s) Molecular Shape N;Lewis Structures, Shapes, and Polarity W 319 Everett Community College Student Support Services Program Draw Lewis structures, name shapes and indicate polar or nonpolar for the following molecules a CH 4 b NCl 3 c CCl 2 F 2 d CF 2 H 2 e CH 2 O f CHN g PI 3 h N 2 O i SO 2 j CS 2 k CO l H 2 O m COF 2 n N 2 o O 2 p H 2 q Cl 2 rDraw the molecule (1 point) bent Question 8 Ionic and Covalent Compounds (5 points) Identify each of the following as a covalent compound or ionic compound Then provide either the formula for compounds identified by name or the name
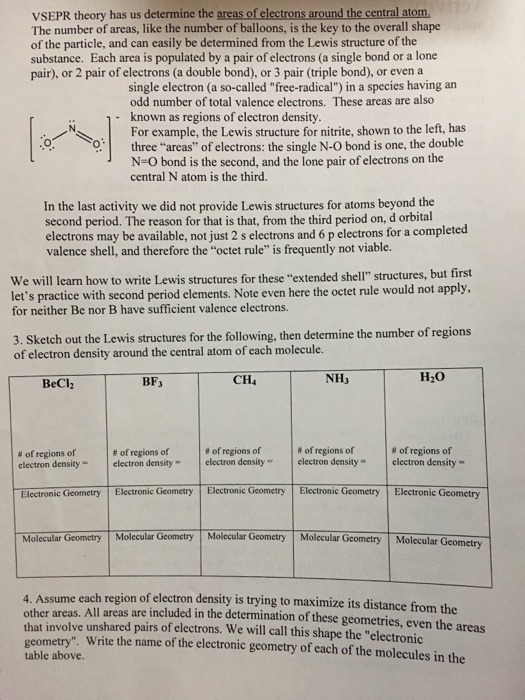


Solved 3 Sketch The Lewis Structure Then Determine The Chegg Com
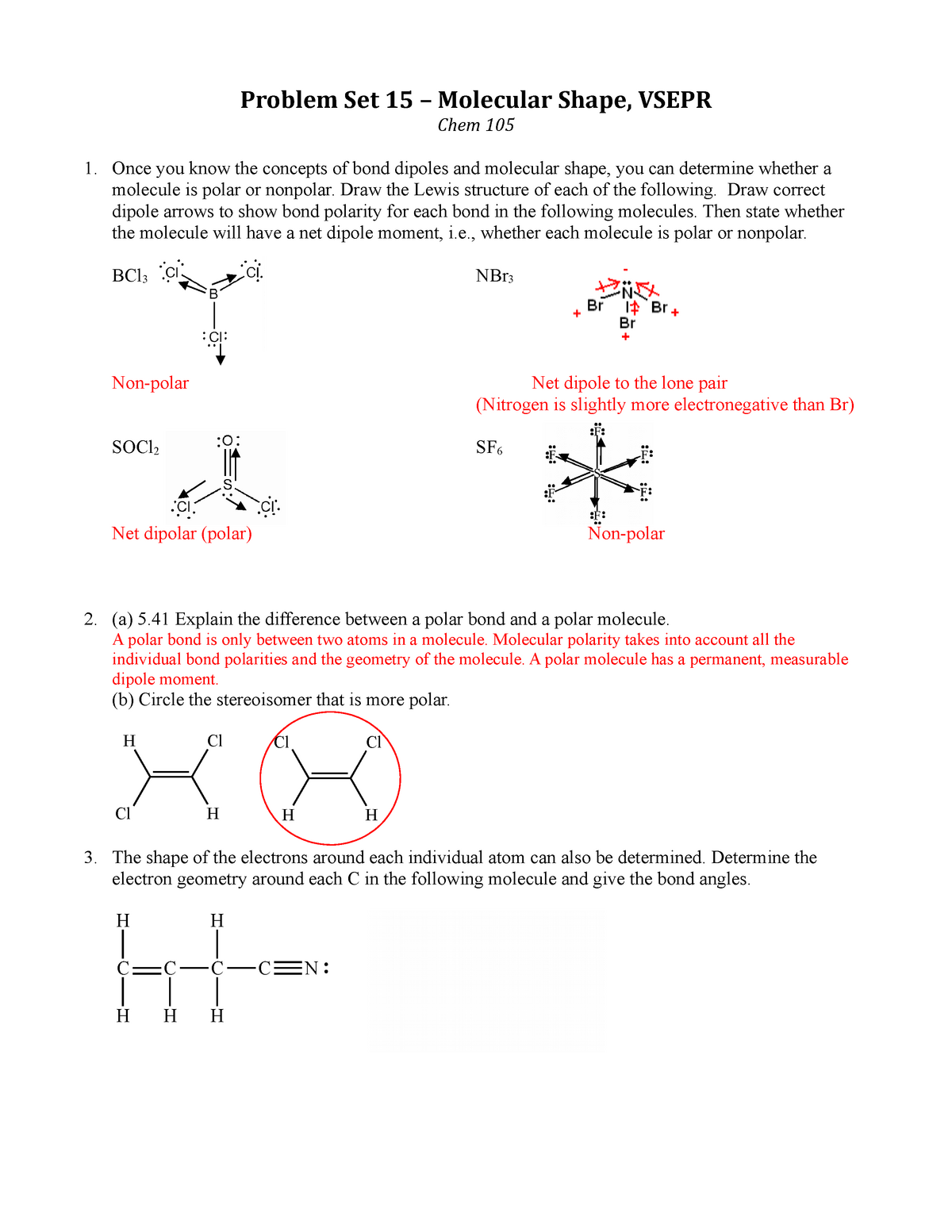


Ps 15 Key Chem 105 General College Chemistry Studocu
Draw the Lewis structure for the SeH 2 molecule (1 point) c What shape would SeH 2 have?Question 4 NO Name Lewis Structure 3D Drawing Hybridization Of Central Atom(s) Bond Angles Molecular Shape Polarity 5 HNO2 Name Lewis Structure 3D Drawing Hybridization Of N;In this example, we can draw two Lewis structures that are energetically equivalent to each other — that is, they have the same types of bonds, and the same types of formal charges on all of the structuresBoth structures (2 and 3) must be used to represent the molecule's structureThe actual molecule is an average of structures 2 and 3, which are called resonance structures



Vsepr Theory Geometry Of Organic Molecules Chemistry Steps



Molecular Geometry Ck 12 Foundation
(15) Use your knowledge of what you've learned so far to provide the Lewis dot structures, electron geometry, molecular shape, bond angles, number of lone pair electrons, and the number of shared pair electrons for each molecule given C I 2 Br 2;Arrangement С O Molecular geometry Overall dipole for molecule?Examples O 2, N 2, C 2 H 4;



Shapes Of Molecules



Molecular Geometry Definition Examples Chemistry Class Study Com
Browse other questions tagged lewisstructure vseprtheory molecularstructure or ask your own questionThe true shape of a molecule is important because it determines many physical and chemical properties for the substance In this activity you will learn how to predict molecular shapes 3D Molecular Shape Model 1 — Lewis Structures Lewis I H 2 CO NH Lone pair — Molecular Geometry H CO 3 electron domain (3 bonding, 0 nonbonding) BeFBond Angles Polarity 6



Answered Draw Lewis Structures For Each Of The Bartleby



Molecular Shape Atomic Combinations Siyavula
SO 4 2Lewis Structure (Sulfate ion) Lewis structure of sulfate ion is drawn in this tutorial step by step Total valence electrons concept is used to draw the lewis structure of SO 4 2In lewis structure of sulfate ion, there should be charges on several atoms due to 2 chargeSH HCOH HN=CH linear Which molecule's Lewis structure contains an atom that violates the octet rule?Question 4 SURVEY 1 seconds Report an issue Q Which of the following is the correct Lewis structure for the compound PBr 3?



Vsepr For 4 Electron Clouds Video Vsepr Khan Academy



Shapes Of Molecules
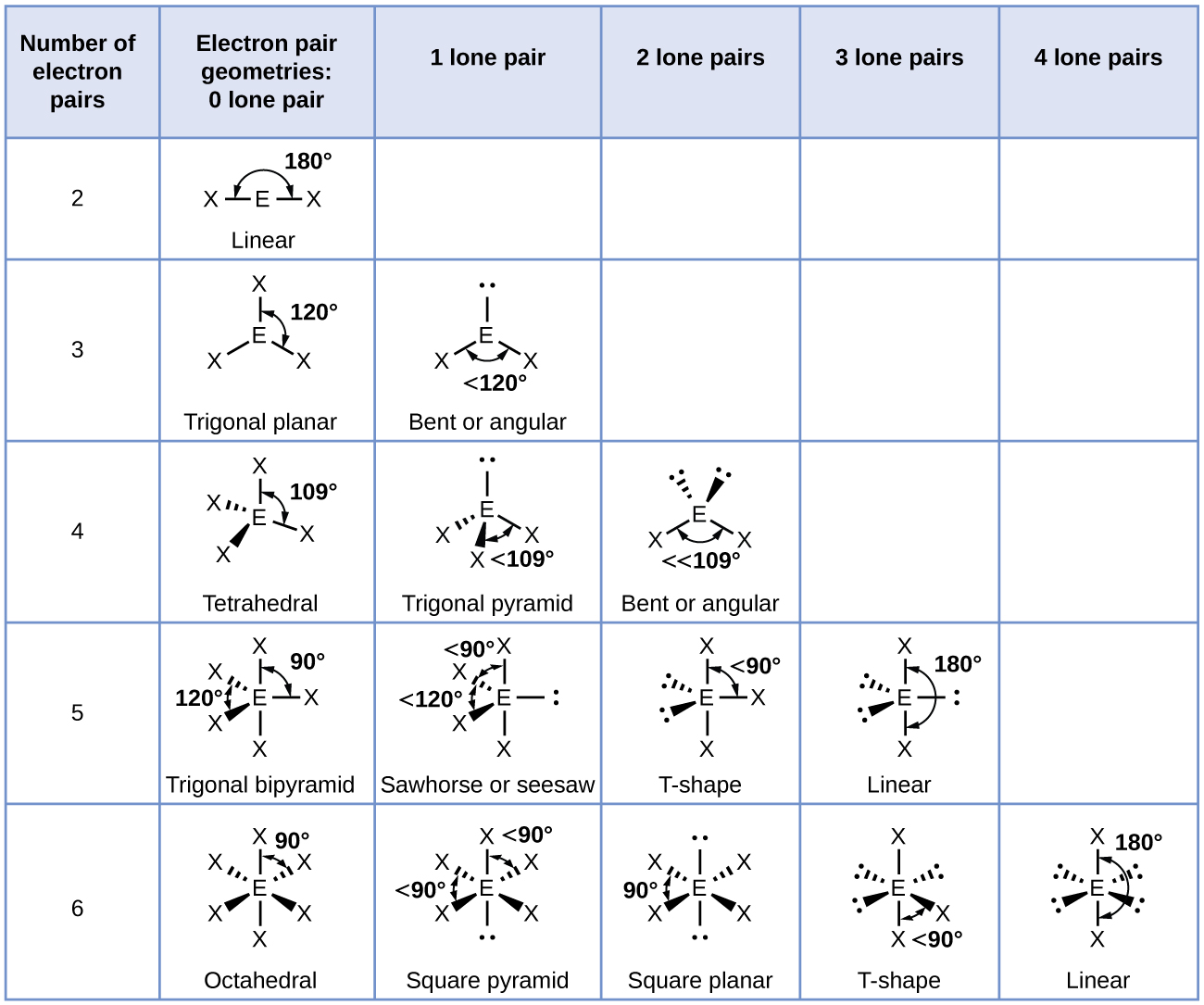
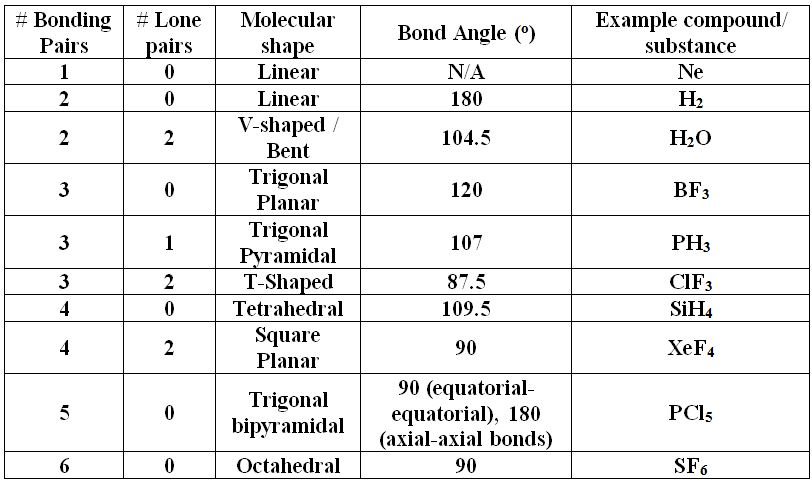
VSEPR Theory Valence shell electronpair repulsion theory (VSEPR theory) enables us to predict the molecular structure, including approximate bond angles around a central atom, of a molecule from an examination of the number of bonds and lone electron pairs in its Lewis structureThe VSEPR model assumes that electron pairs in the valence shell of a central atom will adopt an arrangement thatVideo Drawing the Lewis Structure for PCl 5 For the PCl5 Lewis structure we first count the valence electrons for the PCl5 molecule using the periodic table Once we know how many valence electrons there are in PCl5 we can distribute them around the central atom and attempt to fill the outer shells of each atom There are a total of 40Browse other questions tagged lewisstructure vseprtheory molecularstructure or ask your own question


How Do I Determine The Molecular Shape Of A Molecule Socratic



C6 Molecular Shapes Assignment For Chem 141 Intro Chem Studocu
For each molecule and ion listed below, provide the Lewis structure, then construct the molecule or ion using the molecular model set After construction, describe the shape of the molecule and draw it, labeling the bond angles, and state wheter the molecule is polar or non polar 1 CH 4 A Lewis structure B Drawing of shape (label angles)Write in the name of the molecular geometry for each molecule described below A molecule with two atoms and no lone pairs around the central atom has a _____ shape A molecule with four atoms and no lone pairs around the central atom has a _____shape A molecule that has two atoms and two lone pairs around the central atom has a _____shapeSolution for CH3OH Valence electrons Lewis Structure Electron Model sketch Polar bonds?


Chapter 5 Chemical Compounds An Introduction To Chemistry



Lab Investigation 8 What Shapes Do Molecules Form
Predict the molecular shape and bond angle, and identify the hybrid orbitals for each of the following Drawing the Lewis structure may help you (Type your answer using the format sp3 for sp3) (a) SCl2 molecular shape bond angle ° hybrid orbital (b) NH2Cl molecular shape bond angle ° hybrid orbitalCheck the Formal Charges to make sure you have the best Lewis Structure Explain HowCheck the Formal Charges to make sure you have the best Lewis Structure Explain How
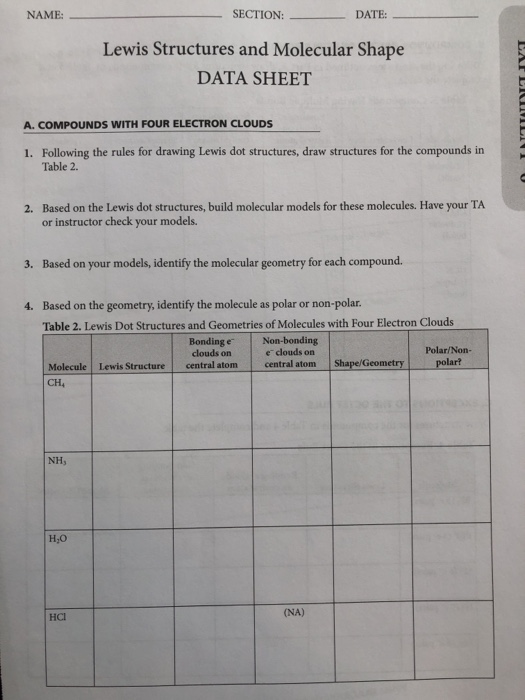


Solved Name Section Date Lewis Structures And M Chegg Com
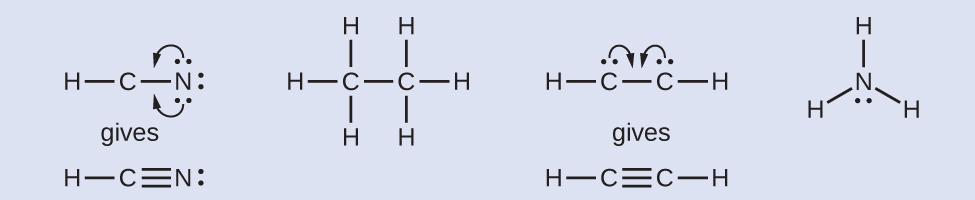


Lewis Symbols And Structures Chemistry 2e
Question 4 SURVEY 1 seconds Report an issue Q Which of the following is the correct Lewis structure for the compound PBr 3?Predicting Molecular Geometry Here is a chart that describes the usual geometry for molecules based on their bonding behavior To use this key, first draw out the Lewis structure for a molecule Count how many electron pairs are present, including both bonding pairs and lone pairsTreat both double and triple bonds as if they were single electron pairsLewis Structures, Shapes, and Polarity W 319 Everett Community College Student Support Services Program Draw Lewis structures, name shapes and indicate polar or nonpolar for the following molecules a CH 4 b NCl 3 c CCl 2 F 2 d CF 2 H 2 e CH 2 O f CHN g PI 3 h N 2 O i SO 2 j CS 2 k CO l H 2 O m COF 2 n N 2 o O 2 p H 2 q Cl 2 r



Javier Hidrogo Cruz Molecular Shape And Polarity Student Pdf 1 Pdf Molecular Shape And Polarity Essential Questions How Does The Number Of Course Hero



Match The Molecular Shapes To The Correct Lewis Structures Options Provided In The Image Below Brainly Com
Drawing the Lewis Structure for PH 3 Video Drawing the Lewis Structure for PH 3 For the PH3 Lewis structure we first count the valence electrons for the PH3 molecule using the periodic table Once we know how many valence electrons there are in PH3 we can distribute them around the central atom and attempt to fill the outer shells of each atomMolecular geometry is the name of the geometry used to describe the shape of a molecule The electronpair geometry provides a guide to the bond angles of between a terminalcentralterminal atom in a compound You should note that to determine the shape (molecular geometry) of a molecule you must write the Lewis structure and determine theQuestion Classify Each Lewis Structure Given Below By Molecular Shape 2 I AX T A XA XAX XA XX XAX XAX Linear Trigonal Planar Tetrahedral Bent Trigonal Pyramidal Other Reset Help This problem has been solved!
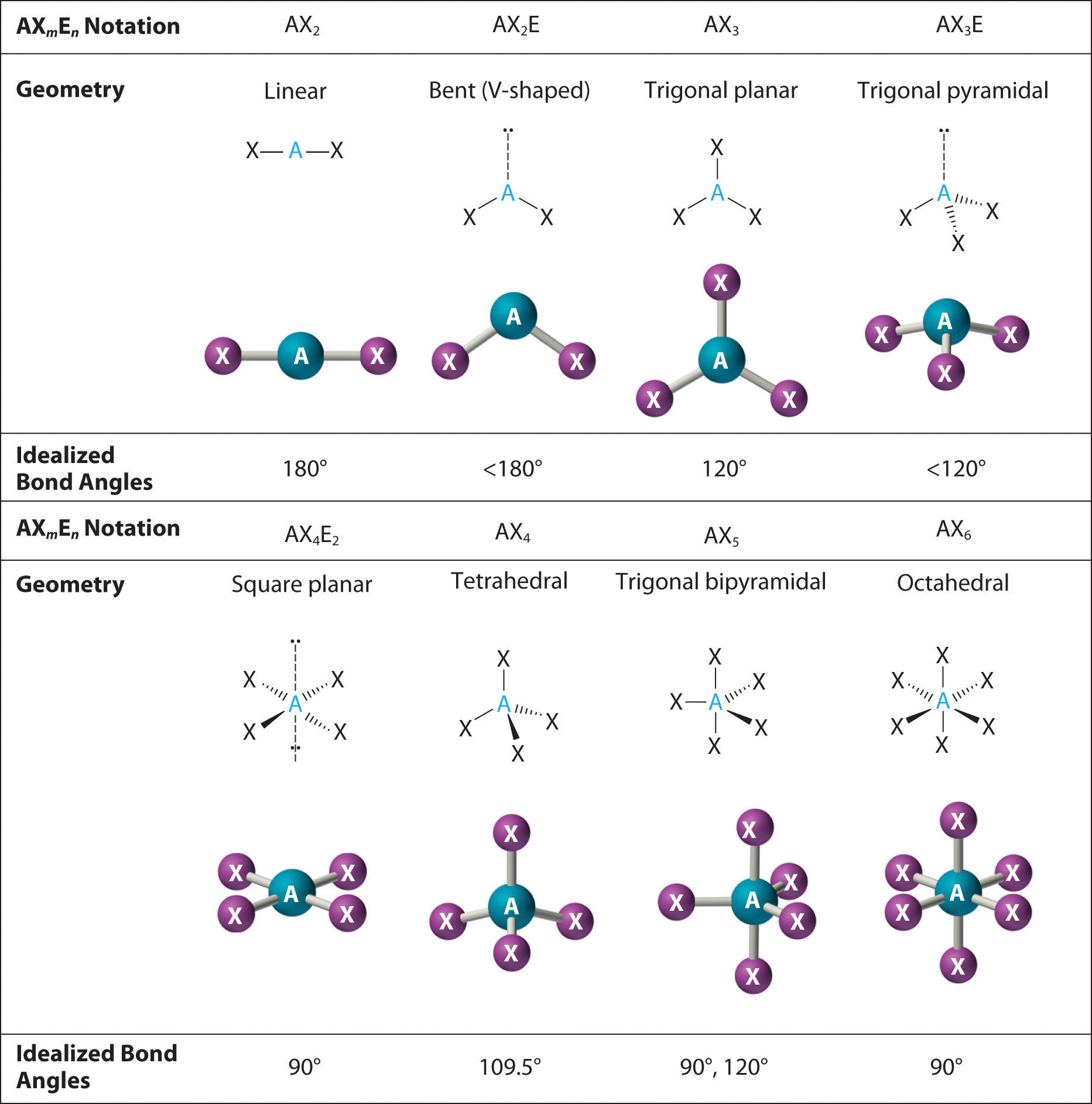


10 3 Vsepr Geometry Chemistry Libretexts



Vsepr Theory Geometry Of Organic Molecules Chemistry Steps
When you draw the lewis structure with Carbon in the middle, and a Chlorine on each side, you will get a single bond from C to each of the Cl's This adds up to 4 single bonds on Carbon 4 bonds on a central atom will give you the "tetrahedral" molecular shape The bond angles for tetrahedral shape are 1095 degreesWrite in the name of the molecular geometry for each molecule described below A molecule with two atoms and no lone pairs around the central atom has a _____ shape A molecule with four atoms and no lone pairs around the central atom has a _____shape A molecule that has two atoms and two lone pairs around the central atom has a _____shapeAnswer choices structure A structure B structure C structure D s Question 5 SURVEY 45 seconds Report an issue Q What is the name of the molecular geometry for this Lewis Structure?


Bond Angles And The Shapes Of Molecules In The Previous Section A Shared Pair Of Electrons Was Presented As The Fundamental Unit Of The Covalent Bond And Lewis Structures Were Drawn For Several Small Molecules And Ions Containing Various Combinations



Molecular Geometry Ck 12 Foundation
A compound with a molar mass of about 28 g/mol contains 857% carbon and 143% hydrogen by mass Write the Lewis structure for a molecule of the compound A compound with a molar mass of about 42 g/mol contains 857% carbon and 143% hydrogen by mass Write the Lewis structure for a molecule of the compound13 Reservation of Rights;Drawing the Lewis Structure for HNO 3 Video Drawing the Lewis Structure for HNO 3 The HNO3 Lewis structure is best thought of as the NO3 with an H attached to one of the oxygen atoms This is a pattern seen with many acids For the HNO3 Lewis structure, calculate the total number of valence electrons for the HNO3 molecule
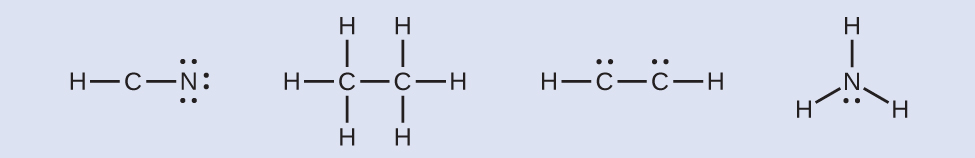


Lewis Symbols And Structures Chemistry 2e
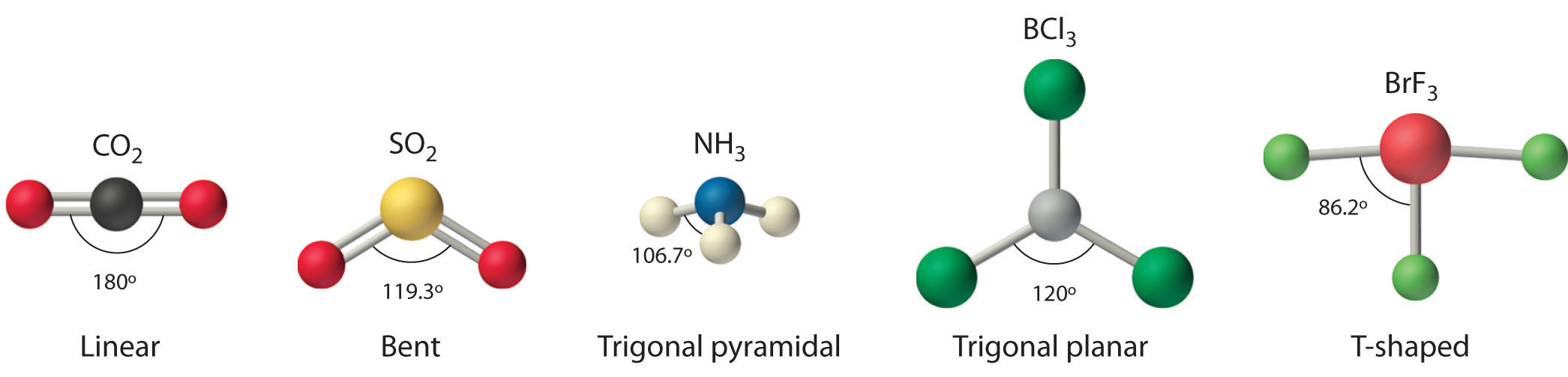


9 7 The Shapes Of Molecules Chemistry Libretexts
I had to draw the molecular shape for $\ce{NHF2}$ as a Trigonal Planar like this Please be sure to answer the question Provide details and share your research!In this example, we can draw two Lewis structures that are energetically equivalent to each other — that is, they have the same types of bonds, and the same types of formal charges on all of the structuresBoth structures (2 and 3) must be used to represent the molecule's structureThe actual molecule is an average of structures 2 and 3, which are called resonance structuresAnswer choices structure A structure B structure C structure D s Question 5 SURVEY 45 seconds Report an issue Q What is the name of the molecular geometry for this Lewis Structure?



Vsepr Theory
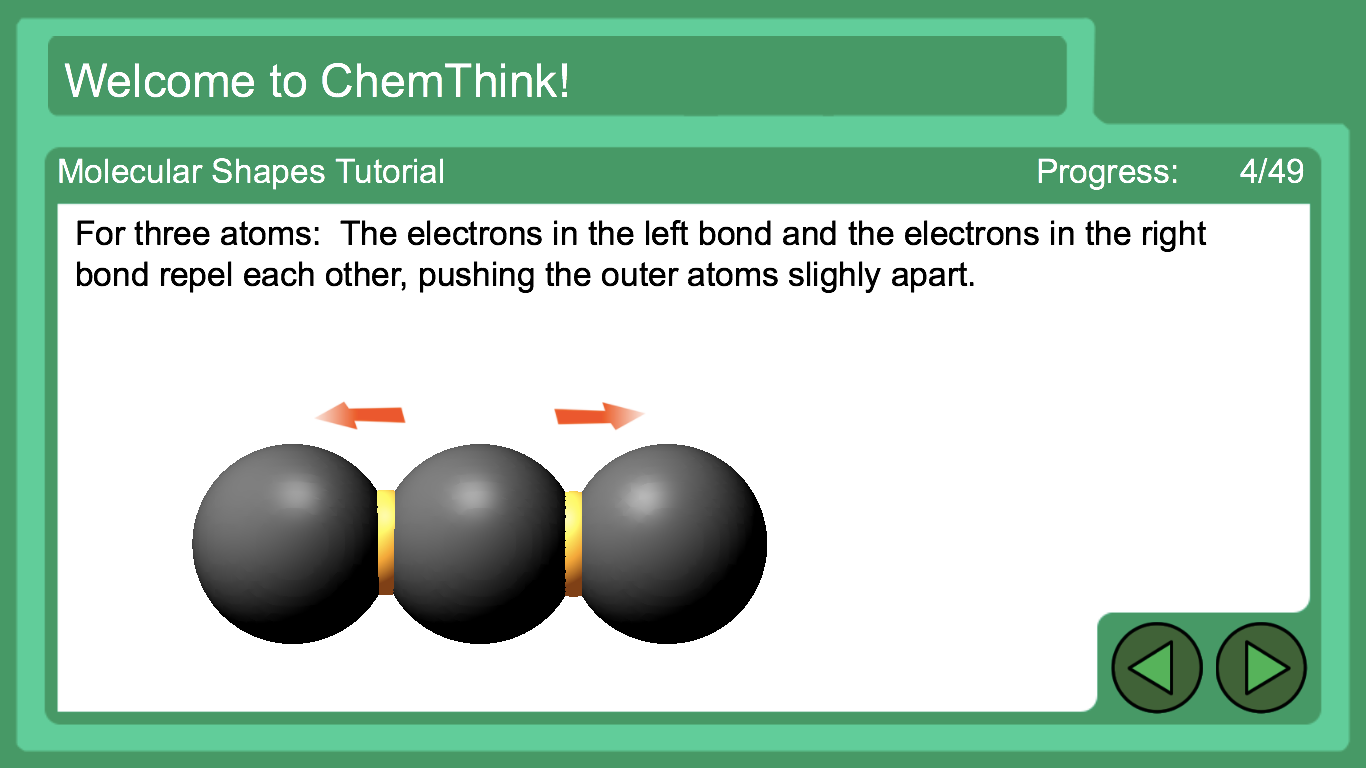


Molecular Shapes Pbs Learningmedia
The lewis dot structure for methane The four hydrogen atoms are equidistant from each other, with all bond angles at 1095° A trigonal bipyramidal shape forms when a central atom is surrounded by five atoms in a moleculeA compound with a molar mass of about 28 g/mol contains 857% carbon and 143% hydrogen by mass Write the Lewis structure for a molecule of the compound A compound with a molar mass of about 42 g/mol contains 857% carbon and 143% hydrogen by mass Write the Lewis structure for a molecule of the compoundDraw the best Lewis Dot Structure for each of the following species a) BeF 2 b) BCl 3 c) CCl 4 d) PBr 5 e) SI 6 Give the name of the electronic arrangement and the name for the molecular geometry for each of the species in question #1 Draw the best Lewis Dot Structures for each of the following species a) BH 2 – b) NI 3 c) ClF 4 d) SF 5 –



E Elecular Geometry Name Pre Laboratory Review Questions And Exercises Due Before Lab Begins Answer In Space Homeworklib
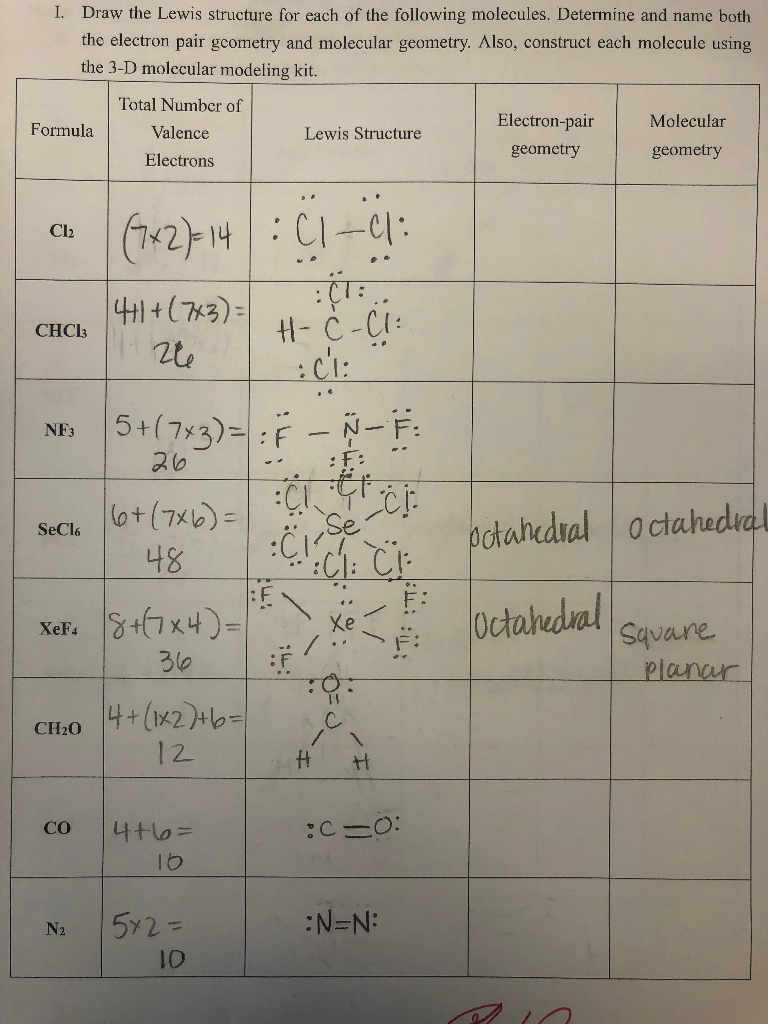


Solved Draw The Lewis Structure For Each Of The Following Chegg Com
Name(s)_____ CHM 10 Lab 06/06/19 Week 4 Assignment a, b, and c Atomic Structure, Chemical Bonding, Lewis Structure, and 3D Molecular Shape Objectives In this lab, you will apply valence bond theory to draw appropriate Lewis structures, use electronegativity differences to classify bonds as ionic, polar covalent, or nonpolar covalentIdentify the following molecular shapes (05 points per answer) n Question 7 Lewis Structure (3 points) a Draw the Lewis structure for the Se and 2 H atoms (1 point) 1)Se < when drawing Lewis dot diagram structure, we consider the number of valance electron of the atom Se has six valance electrons since it is in group size thus its Lewis dot diagram is as followsTwo dashed lines indicate two shared pairs, or one sigma bond and one pi bond Unshared pairs of electrons are represented by two dots Unshared pairs go where they are needed The objective of every atom in a Lewis structure is to have an octet, or eight electrons Please refer to the attached image to help answer the questions



3 Draw A Lewis Structure For Co2 Draw All If More Than One Resonance Structure Is Possible 4 Predict The Molecu Homeworklib


7 E Chemical Bonding And Molecular Geometry Exercises Chemistry Libretexts
They simply show the number and types of bonds For example, the Lewis structure of CCl 4 tells us only that four Cl atoms are bonded to a central C atomI had to draw the molecular shape for $\ce{NHF2}$ as a Trigonal Planar like this Please be sure to answer the question Provide details and share your research!Lewis Structures, Shapes, and Polarity W 319 Everett Community College Student Support Services Program Draw Lewis structures, name shapes and indicate polar or nonpolar for the following molecules a CH 4 b NCl 3 c CCl 2 F 2 d CF 2 H 2 e CH 2 O f CHN g PI 3 h N 2 O i SO 2 j CS 2 k CO l H 2 O m COF 2 n N 2 o O 2 p H 2 q Cl 2 r
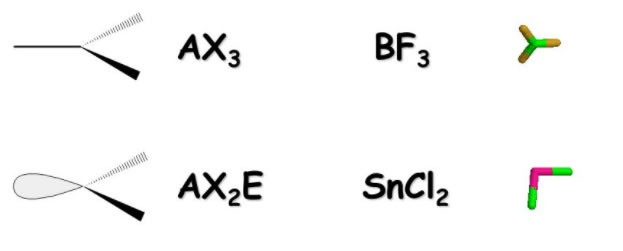


Molecular Formulas And Nomenclature



Chapter 6 Molecular Structure
In this example, we can draw two Lewis structures that are energetically equivalent to each other — that is, they have the same types of bonds, and the same types of formal charges on all of the structuresBoth structures (2 and 3) must be used to represent the molecule's structureThe actual molecule is an average of structures 2 and 3, which are called resonance structuresCF4 XeF4 ClF3 (a) Draw a Lewis electrondot structure for each of the molecules above and identify the shape of each (b) Use the valence shell electronpair repulsion (VSEPR) model to explain the geometry of each of these molecules CF4 4 bonding pairs around the C at corners of regula r tetrahedron to minimize repulsion (maximize bond angles)
/lewis-fc84e3f1452e4aacb2fe023cfff2fa08.jpg)


Lewis Structure Example Problem Formaldehyde



Lewis Symbols And Structures Chemistry I



Identify The Molecular Shape Of Each Lewis Structure Brainly Com



Molecular Structure Exercises



Solved 4 For Each Of The Species Below 1 Draw The Lew Chegg Com
/Lewis-dot-structure-58e5390f3df78c5162b4c3db.jpg)


How To Draw A Lewis Structure
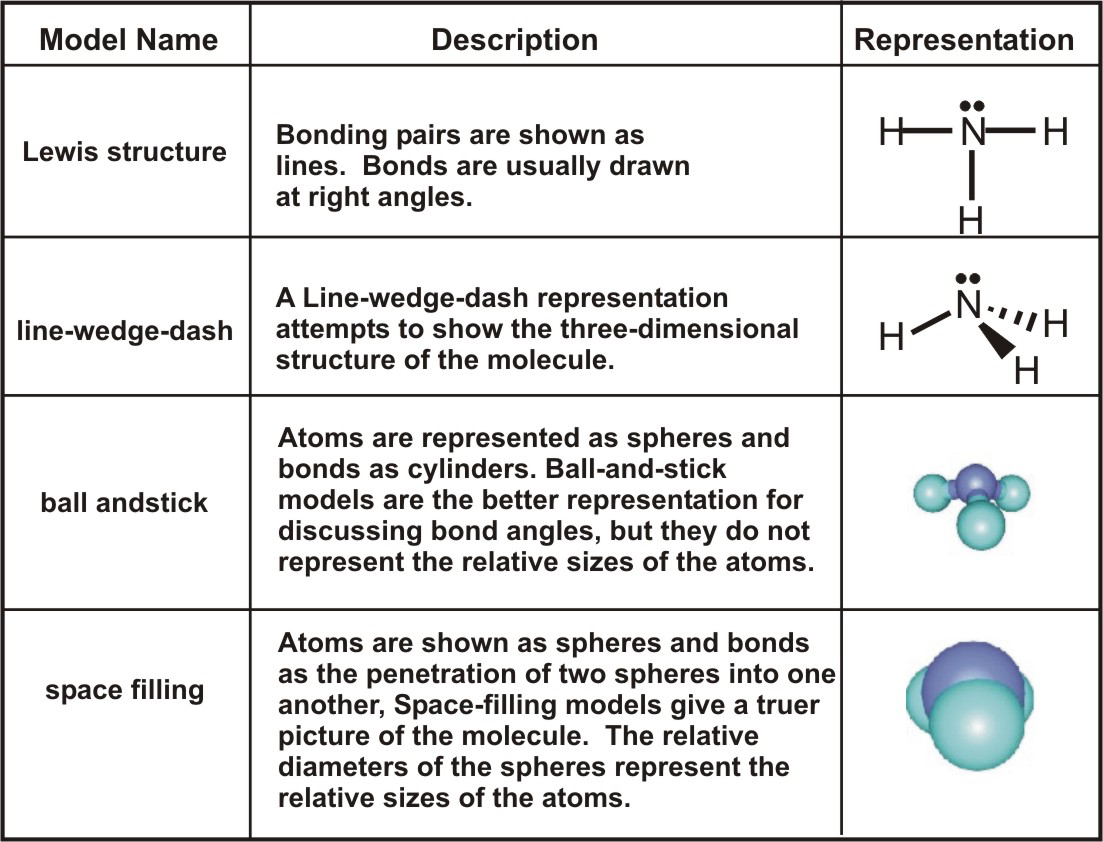


Chapter 6 Molecular Structure



Oneclass Scantron Name Mad The Lewis Structures Of The Molecules Below And Use Them To Answer The Fo
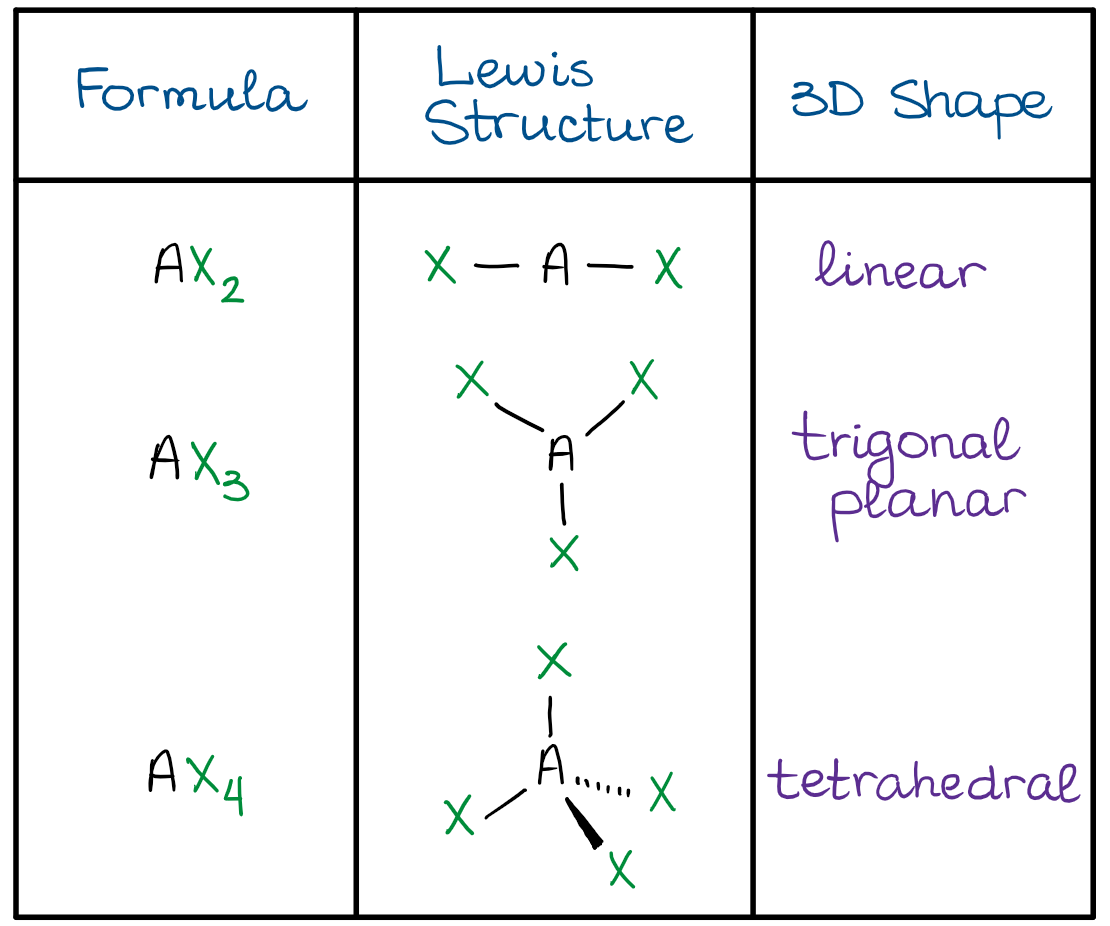


Vsepr Theory Organic Chemistry Tutor



Vsepr For 2 Electron Clouds Video Vsepr Khan Academy



3 Write Lewis Structures For The Following What Molecular Shape Does Each Have Circle The Structures Homeworklib



Write Down Lewis Structure Of Sbr4 And Pro Clutch Prep
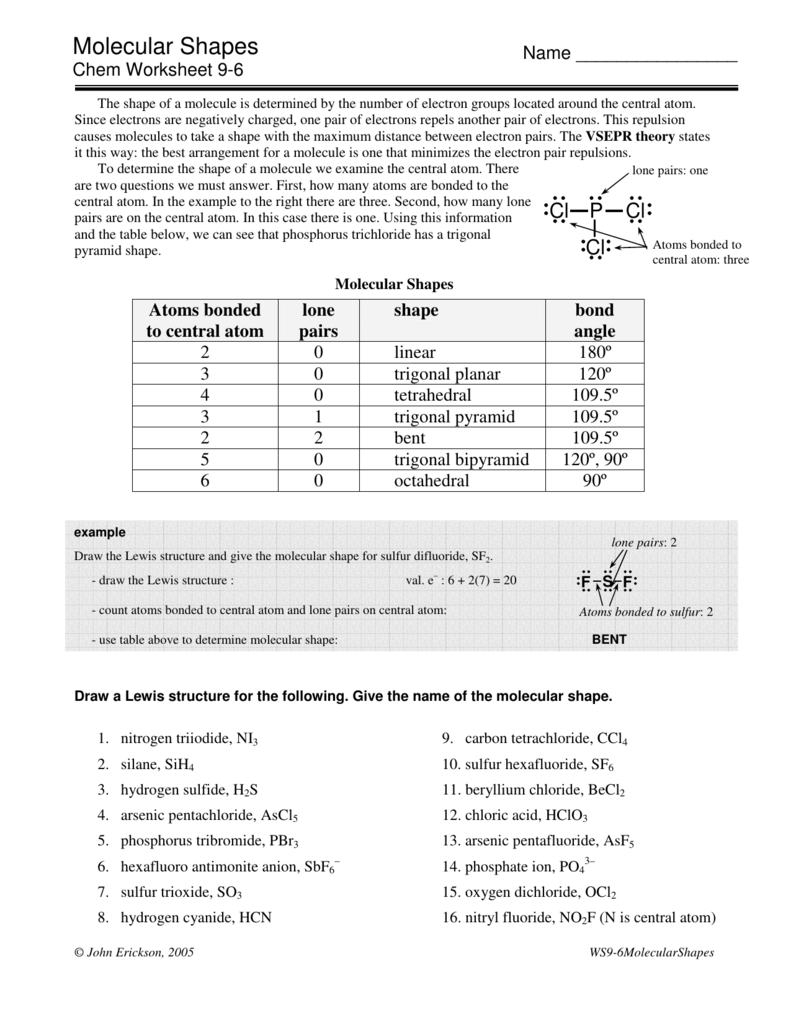


Predicting Molecular Shapes



The Vsepr Theory To Predict The Electronic And Molecular Geometry
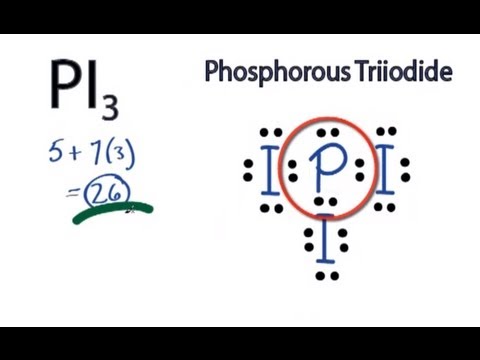


Based On The Vsepr Theory What Is The Molecular Geometry Of A Molecule Of Pi3 Socratic


Predicting The Geometry Of Molecules And Polyatomic Ions



Ch3oh Molecular Geometry Shape And Bond Angles Methanol Youtube



Chapter 10 Flashcards Quizlet


5 2 Molecular Shape Chemistry Libretexts


Predicting The Geometry Of Molecules And Polyatomic Ions



Solved 1 Name And Chemical Formula Methane Ch4 Lewis Str Chegg Com



Molecular Geometry Boundless Chemistry



Molecular Geometry Lab Word


Chapter 5 1 Predicting The Geometry Of Molecules Chemistry Libretexts



Hydrocarbons Introductory Chemistry



Vsepr Model



Solved Directions For Each Of The Following Compounds Na Chegg Com



Po3 3 Molecular Geometry Shape And Bond Angles Youtube


Molecular Geometry Studypug



The Structure Of Tef 5 Isdraw A Complete Clutch Prep
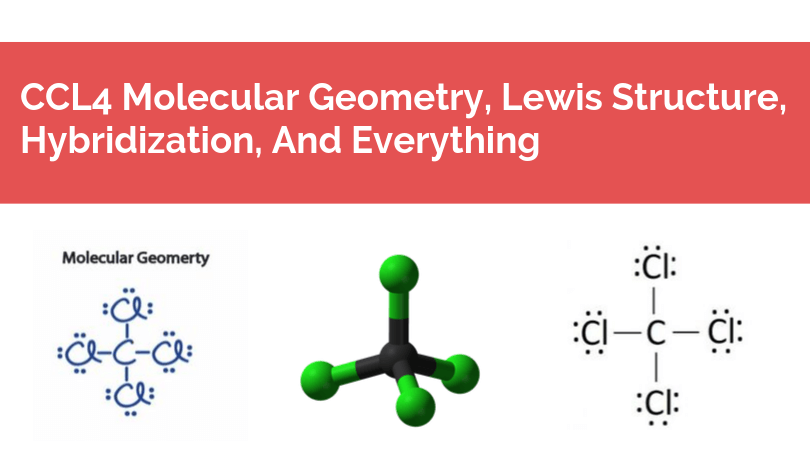


Ccl4 Molecular Geometry Lewis Structure Hybridization And Everything



Solved Name 3 Draw A Lewis Structure For Sfst Draw All Chegg Com


Chem 101 Lewis Structures
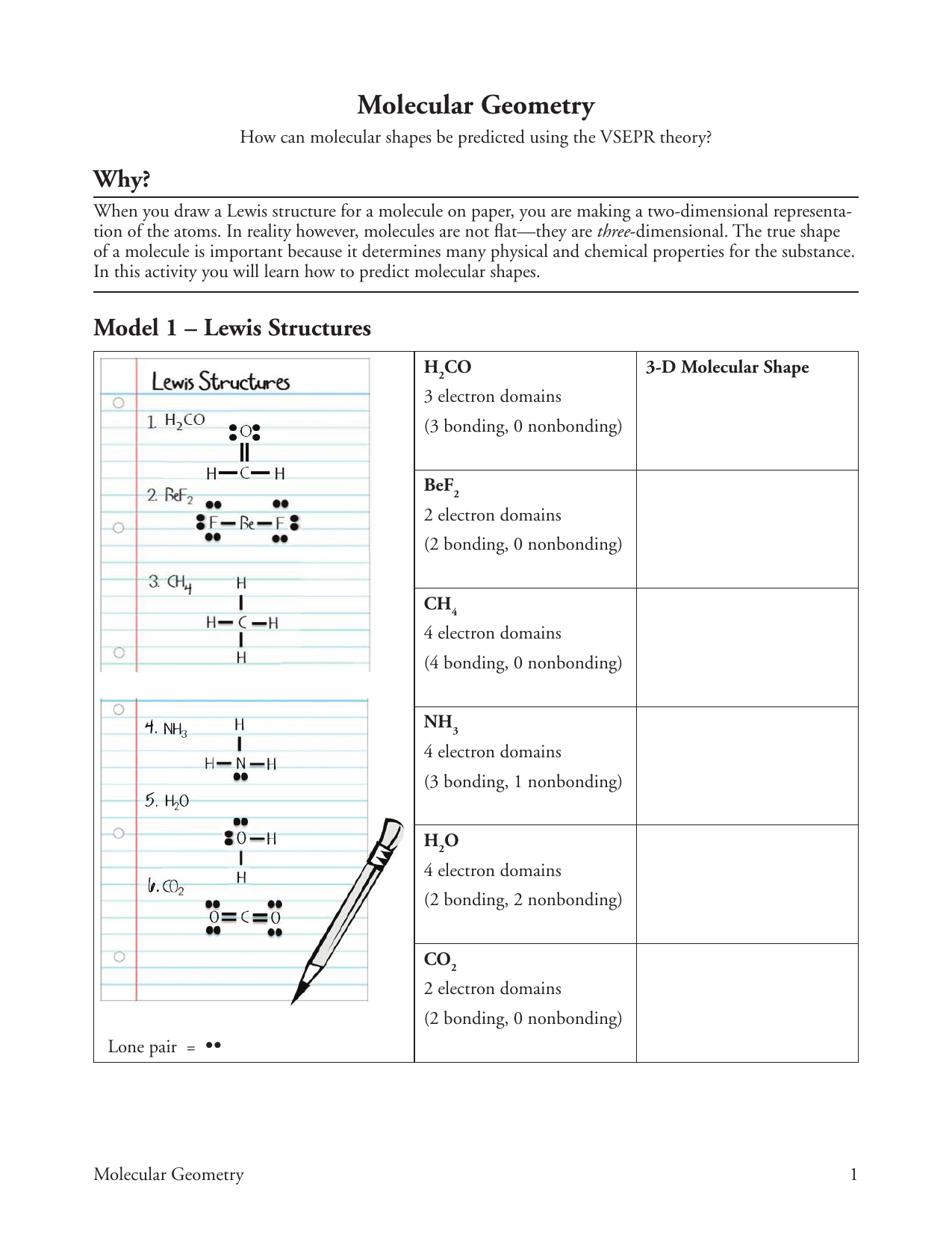


3 7 Pogil Molecular Geometry



Molecular Geometry Boundless Chemistry



Chapter 12 Molecular Structure An Introduction To Chemistry


Chem 101 Octet Rule Violations
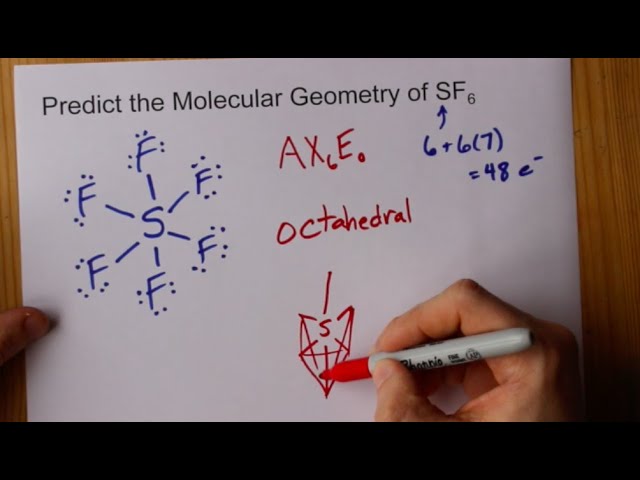


Molecular Geometry Of Sf6 Sulfur Hexafluoride Youtube



Tetrahedral In Molecular Geometry Definition Structure Examples Geometry Class Video Study Com



Cnem 11 Experiment 7 Pre Lab Answer The Following Questions And Consult Your Textbook Or Lecture Notes Homeworklib



Vsepr Theory What Is It Importance Limitation Notation Videos Q A



Drawing Dot Structures Video Khan Academy



Solved Determine The Lewis Structure And Molecular Shape Chegg Com
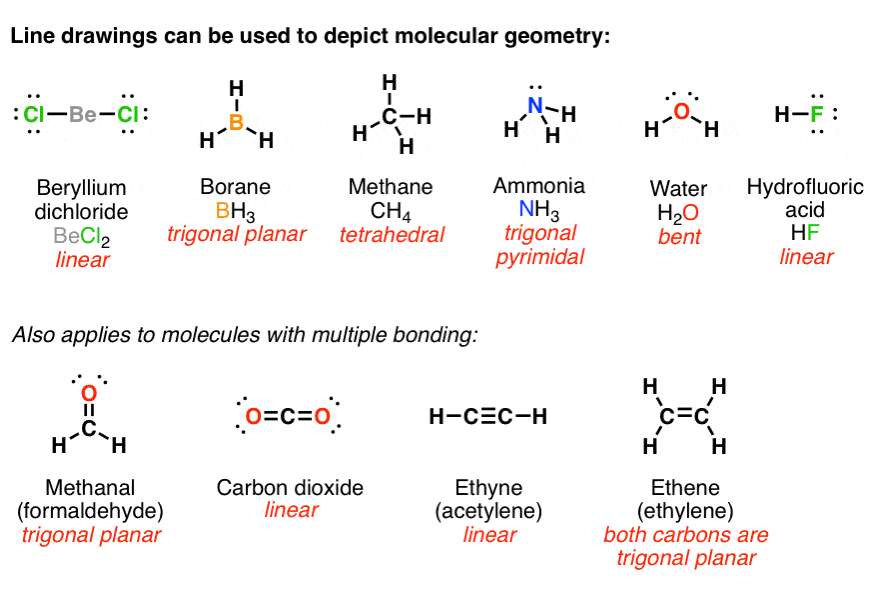


From Gen Chem To Org Chem Pt 7 Lewis Structures Master Organic Chemistry
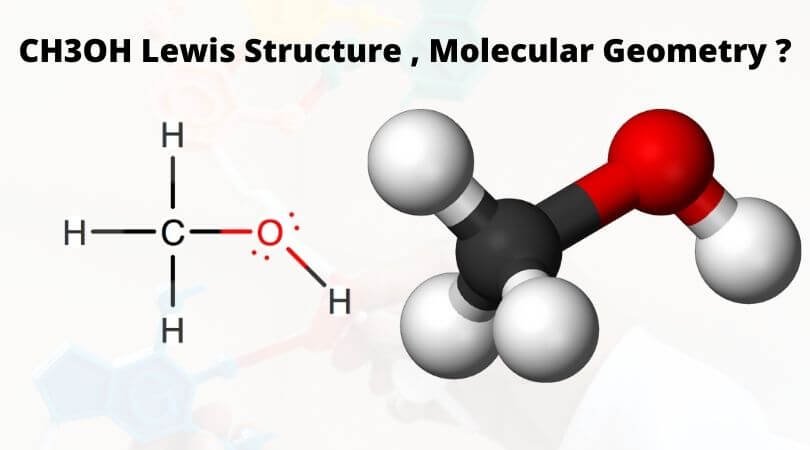


Ch3oh Lewis Structure Molecular Geometry And Shape Geometry Of Molecules
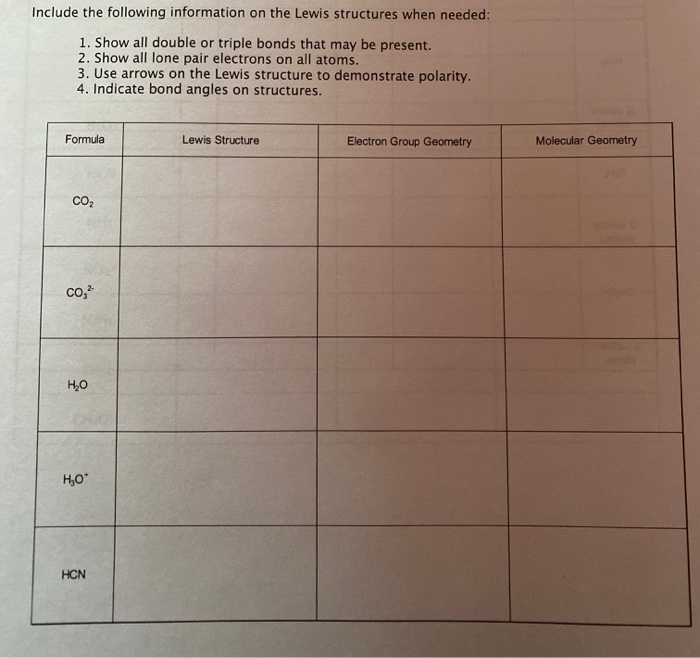


Solved Include The Following Information On The Lewis Str Chegg Com



Vsepr Theory What Is It Importance Limitation Notation Videos Q A
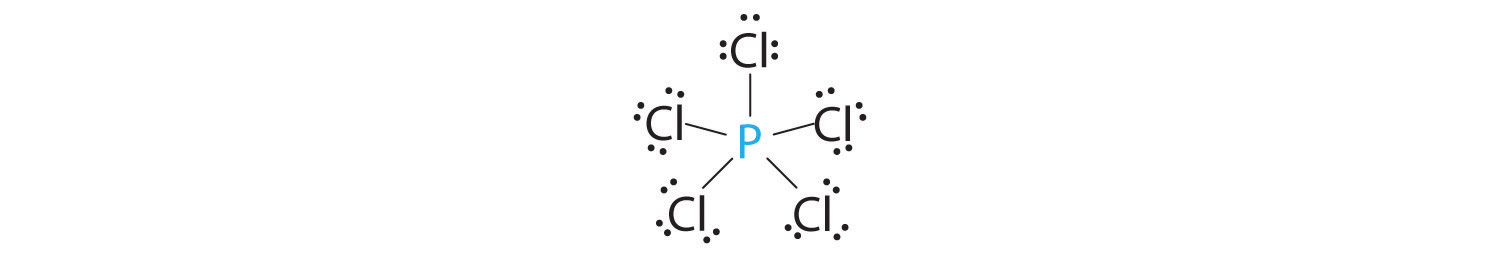


Chapter 5 1 Predicting The Geometry Of Molecules Chemistry Libretexts
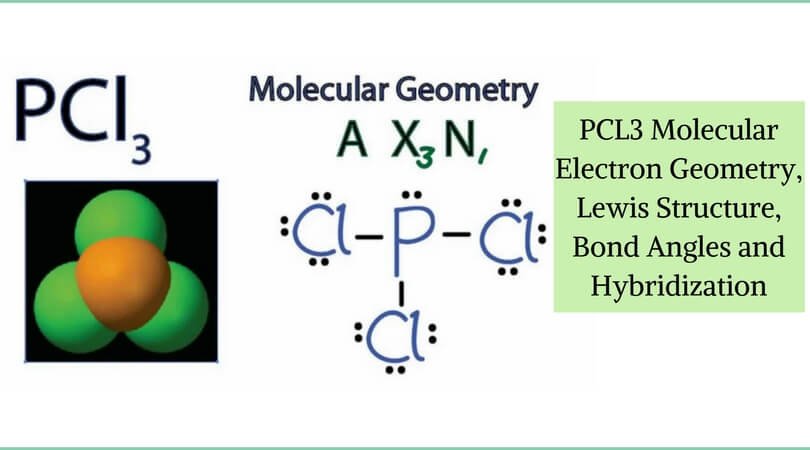


Pcl3 Molecular Electron Geometry Lewis Structure Bond Angles And Hybridization
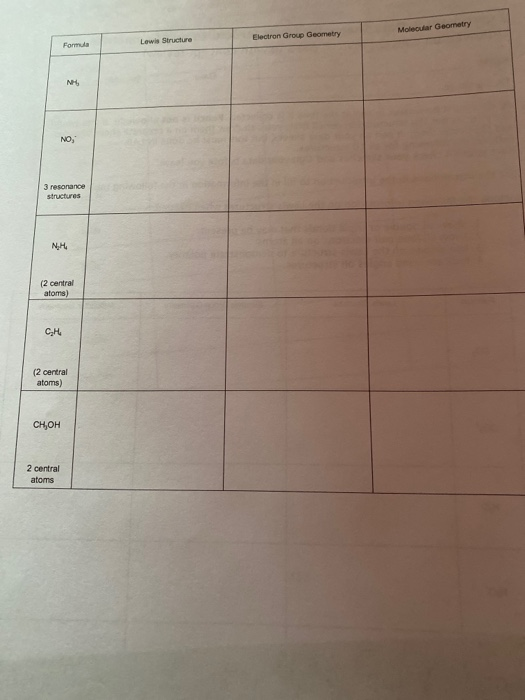


Solved Include The Following Information On The Lewis Str Chegg Com



Bonding And Imfs Flashcards Quizlet


